the dam at Timber Lake washed out in 1995, and was rebuilt two years later
Source: ESRI, ArcGIS Online

the dam at Timber Lake washed out in 1995, and was rebuilt two years later
Source: ESRI, ArcGIS Online
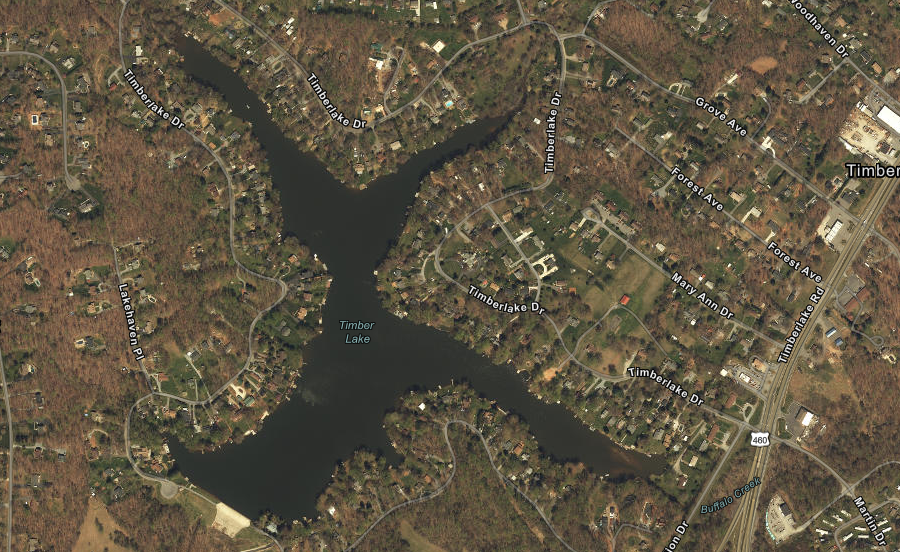
The dam across Buffalo Creek that created the 75-acre Timber Lake was completed in 1926, when a new subdivision was constructed south of Lynchburg.
On June 22, 1995, the dam washed out. A heavy rainstorm dropped over 11" of rain that day, exceeding the total expected in a 100-year storm. Flooding trapped cars on the US 460 bridge over Buffalo Creek. One driver said:1
Sedimentation had reduced the lake to 68 acres when the rain raised the lake level by over eight feet. Water from the lake filled the three, 36-inch pipes that served as the spillway, then overtopped the earthen dam around 8:00pm. At the peak, the water level was 5 feet higher than the dam.
The dam broke at 10:20pm and released a wall of water into Buffalo Creek. The entire lake drained in just one hour. One local resident commented:2
Downstream, rescuers were trying to get people out of cars stalled in the US 460 bridge at border of Bedford and Campbell counties. The Assistant Fire Chief of the Brookville-Timberlake Volunteer Fire Department, Carter Martin, tied a rope around his body and went into the floodwaters to a car whose brake lights had flashed after a call from the fire truck's public address system.
When the dam broke, a wave of water flooded over the US 460 bridge. Firefighters holding Carter Martin's lifeline backed up enough to retain their footing, but he was swept downstream. Even the ladder truck, to which the line was attached, moved several feet.
Backing up truck to pull Martin out of the water was delayed because another vehicle belonging to the Lynchburg Lifesaving Crew was parked behind it, and the keys were with rescuers in a boat trying to reach trapped vehicles. By the time the fire truck could move and pull Carter Martin from the water, he had already drowned. The vehicle he had been trying to reach was empty; its occupants had already reached safety before the rescue attempt.
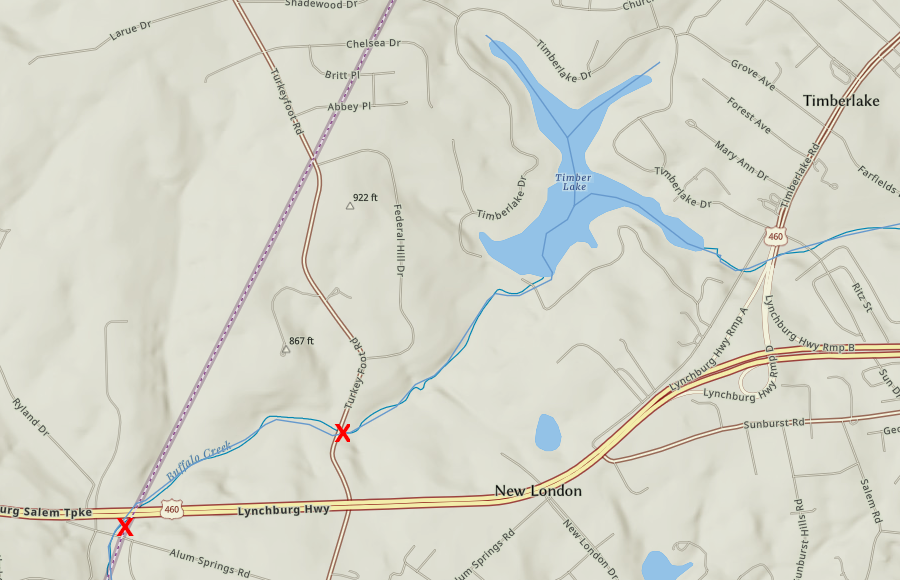
Another person drowned that night in Buffalo Creek. She had chosen an alternative route after US 460 flooded, and was apparently crossing on Turkey Foot Road when the wall of water overwhelmed her vehicle. Her body was found three days after the dam broke.3
two people drowned when the Timber Lake dam broke
Source: ESRI, ArcGIS Online
The value of homes near Timber Lake dropped 35-50% after the lake drained. Residents in the Timberlake Homeowner's Association rejected proposals to convert the lake into a golf course. Instead, they raised nearly two million dollars, in part through a Small Business Administration loan, and built what they named the Carter D. Martin Memorial Dam.4
The dam was rebuilt to withstand another rainfall event comparable to the night of June 22, 2019. That was estimated to be half of a Probable Maximum Flood, which would be triggered by the largest rainfall event reasonably prdedicted for that site.
In 1996, the remnants of Hurricane Fran passed over Campbell County as the new dam was partially completed. A local resident recorded:5
After Virginia updated its dam safety standards in 2008, the new structure was classified as a High Hazard Dam. Calculations showed that rainfall could produce a Maximum Probable Flood with water levels reeaching 820.9 feet, which was 1.6 feet higher than the dam. Water overtopping the dam, unable to flow through the concrete spillway, could erode the earthen barrier and cause another catastrophic failure.6
The Timber Lake dam withstood the August 2, 2018 storm that caused Lynchburg officials to evacuate 150 people downstream of College Lake. The homeowners association lowered the lake that Fall to facilitate repair of docks, and to assess how to dredge the accumulated sediment. The president of the Timberlake Homeowners Association made clear that Timber Lake would be maintained rather than drained:7
To meet dam safety regulations, the Timberlake Homeowners Association planned to expand the capacity of the emergency spillway. It also proposed a major project to remove sediment which had accumulated in the five coves where streams enter Timber Lake.
In 1997, 70,000 cubic yards of silt were moved within the lake to a deeper portion to facilitate recreational use. The Timberlake Homeowners Association would have preferred to remove it, but cost was excessive. No one accepted to opportunity to haul it away for free.
The silt reflected how a once-rural watershed had been transformed into suburbia, and the erosion associated with construction of impervious surfaces. Leaders in the Timberlake Homeowners Association pressed Campbell County officials to limit new development upstream of the lake, to mininmize additional silt transport.8
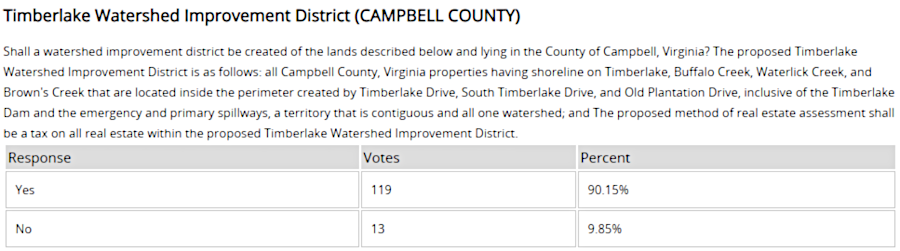
The homeowners association worked with the Robert E. Lee Soil and Water Conservation District to create a Watershed Improvement District. That entity could collect a tax on all property owners within its boundary, in order to finance spillway expansion and what was expected to be the largest inland dredging project in the state. Virginia's first Watershed Improvement District had been created after Hurricane Agnes damaged the Lake Barcroft dam in 1972.9
On April 2, 2019, the Watershed Improvement District was approved in a special referendum. Of the 250 residents eligible to vote, 132 cast a ballot and approved the district by a 90-10 percentage.
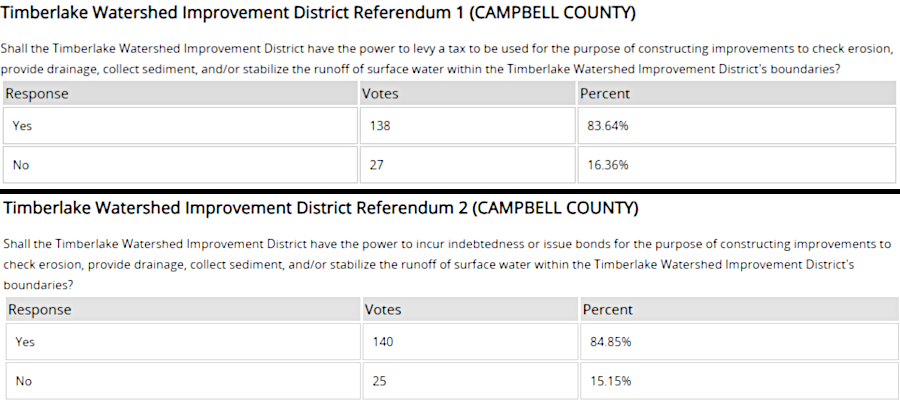
The estimated cost for the dredging was $500,000, roughly $2,000 per resident living within the boundaries of the proposed district. In the 2019 general election, the residents living within the boundaries of the Timberlake Watershed Improvement District authorized it to levy a tax to finance lake manaintenance. The approval by 84% of the voters demonstrated the community support to keep Timber Lake useful for recreation by the landowners.10
the April 2, 2019 referendum to create the Timberlake Watershed Improvement District was approved by an overwhelming margin
Source: Virginia Department of Elections, 2019 April 2 Special - Official Results
the November 5, 2019 referendum authorized the Timberlake Watershed Improvement District to tax real estate and issue bonds in order to finance Timber Lake maintenance
Source: Virginia Department of Elections, 2019 November General - Official Results
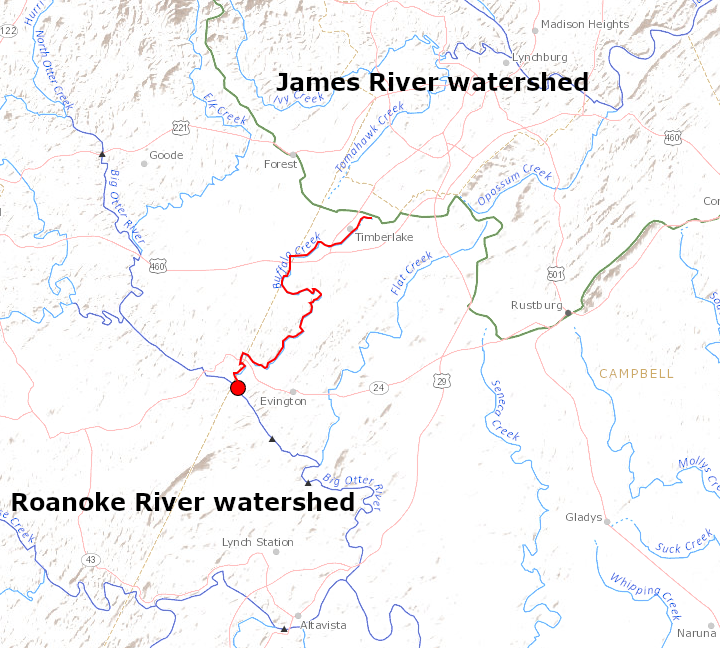
a dam on Buffalo Creek (red) created Timber Lake near the watershed divide separating the James and Roanoke rivers
Source: US Geological Survey (USGS), Streamer