
pumping sand that was dredged from the bottom of the Chesapeake Bay onto Ocean View Beach
Source: US Army Corps of Engineers, Norfolk District Image Gallery

pumping sand that was dredged from the bottom of the Chesapeake Bay onto Ocean View Beach
Source: US Army Corps of Engineers, Norfolk District Image Gallery
Beaches are dynamic, not static. Sand particles are always moving, with the alignment rearranged by wind and water. Large storms can erode a beach completely, or deposit a new sand spit. A quarter of Virginia's shoreline is eroding, and some sites in Virginia are losing land at a rate of 30 feet per year.1
Bulkheads, jetties, and "living shorelines" can alter the movement of sand temporarily. Beach replenishment is another temporary solution. Replenishment projects are based upon the assumption that after storms move sand, humans can pump/dump sand to restore the beach.
Future storms will move the sand again, and future replenishment projects will rebuild the beach again. Rather than fight the natural flow of sand, local/state/Federal budgets set aside funds to pay for regular replenishment. Virginia Beach now routinely plans to replenish sand at Chesapeake Beach, Sandbridge, and in the Oceanfront resort area. The city estimates that wider beaches avoided up to $1 billion in storm-related damages between 2002-2024.
In 2002 the US Congress authorized the Beach Erosion Control and Hurricane Protection Project partnership between the City of Virginia Beach and the US Army Corps of Engineers. Signing of a Project Cooperation Agreement between the city and Corps of Engineers in 2002 established a 65% Corps - 35% city ratio for funding projects, but Federal funding has not always been appropriated.
The city funded 100% of the initial beach nourishment project at Sandbridge in 1998. The fifth project in 2020, placing 1.7 million cubic yards of sand on the five miles of beach between Back Bay National Wildlife Refuge and Dam Neck Naval Facility, cost $20.3 million. Because the US Congress appropriated only $3 million, the Sandbridge Special Service District funds covered 85% of the cost.
At Chesapeake Beach, a 2028 project renewed the dune system and enhanced the beach berm profile with 384,000 cubic yards of sand. A renourishment in 2024 added almost 140,000 cubic yards between Lee Avenue and the Joint Expeditionary Base Little Creek. Sand replenishment at the Oceanfront (with most of the tall resort hotels) is planned for every five to seven years. After a 2013 project, a new one in 2019 placed 1.4 million cubic yards of sand between 15th-70th Street. Enough sand was added to the Oceanfront to widen the shoreline back to 300 feet and increase it to 9 feet above sea level. Dredging of the Atlantic Ocean Channel for the Norfolk Harbor Deepening Project provided the sand for replenishment.
The Corps of Engineers sourced sand from the Atlantic Ocean Channel again in 2024-25 from the "Wider, Deeper, Safer” dredging project for another beach replenishment project to add 950,000 cubic yards at the Oceanfront and on Croatan Beach south of Rudee Inlet. The Corps continued to fund 65% of the $20 million cost for the 2024-25 project:2

different segments of beach are closed temporarily to public use during beach replenishment at the Oceanfront
Source: City of Virginia Beach, Beach Replenishment
Sand was planned to be added to the resort beach between 15th and 45th streets, but work was halted after sand was placed between 19th and 23rd streets. The sand from the Atlantic Ocean Channel was not "beach quality." Particles were grey and too small.3
After Superstorm Sandy in 2012, the beach in the Ocean View neighborhood of Norfolk was replenished. The Corps of Engineers dredged sand from the Thimble Shoal shipping channel, pumped it onto the Ocean View beach, and spread the sand with bulldozers. The objective was to build a beach 60' wide and 5' high at the landward edge.
Norfolk had tried to maintain the width of the beach by constructing 36 rock breakwaters. Those trapped sand moving along the shoreline, but also disqualified Ocean View from Federal beach replenishment programs. The regulations were revised after Superstorm Sandy.
Congress appropriated $12.9 million and Norfolk contributed $5.5 million for the first replenishment stage, which was completed in 2017. The City of Norfolk contributed 30%, but its future share will be 23%. As reported in The Virginian-Pilot:4
The total $34.5 million dredging and beach building project planned to place 1.2 million cubic yards of sand onto Ocean View. The first phase revealed that some parcels that would be affected were not publicly owned. The city researched deeds and acquired private beachfront parcels. In 2022, Norfolk purchased an eight-acre parcel that Ballard Fish & Oyster Company had owned since 1938.
The property was vacant and the company's clam/oyster farming (Cherrystone Aqua-Farms) was done on the Eastern Shore, but public ownership ensured that the next beach restoration effort at Ocean View could proceed without objection by a private property owner.5
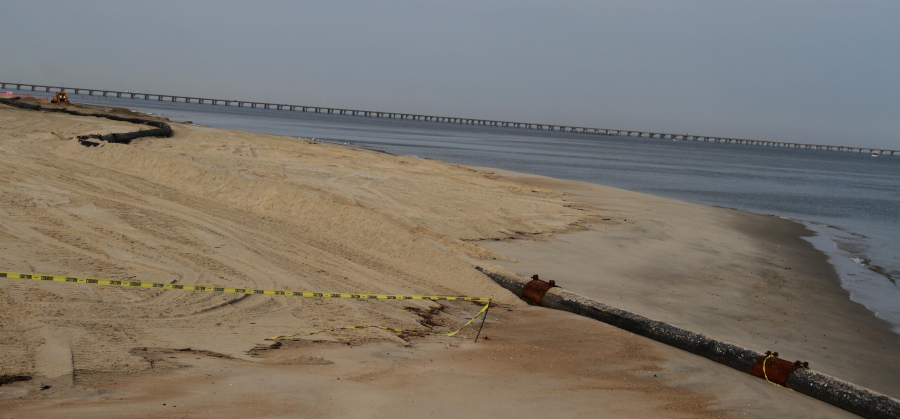

sand dredged from the Lynnhaven Inlet channel after Superstorm Sandy in 2012 was used to replenish the beach from the Lynnhaven Inlet to Chic's Beach
Source: US Army Corps of Engineers, Norfolk District Image Gallery
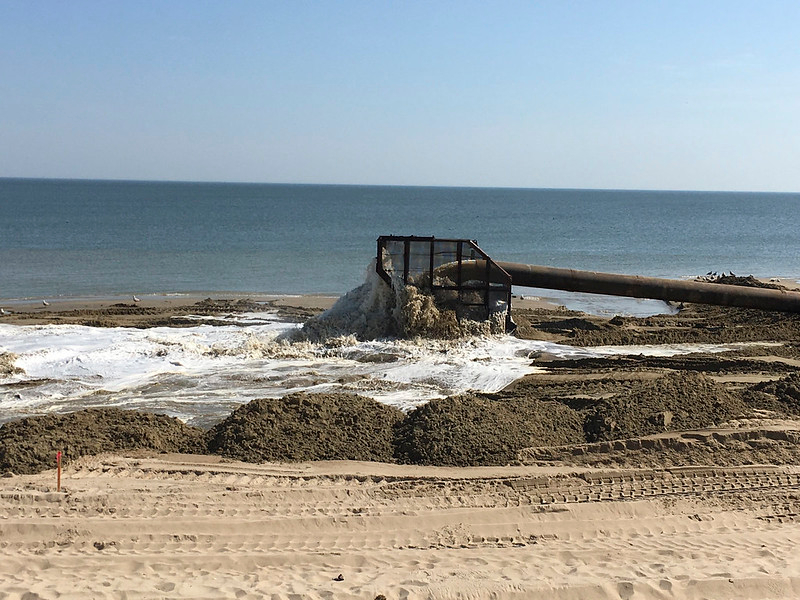

sand was pumped from the bottom of Chesapeake Bay onto the beach at Ocean View
Source: US Army Corps of Engineers, 170428-A-BJ794
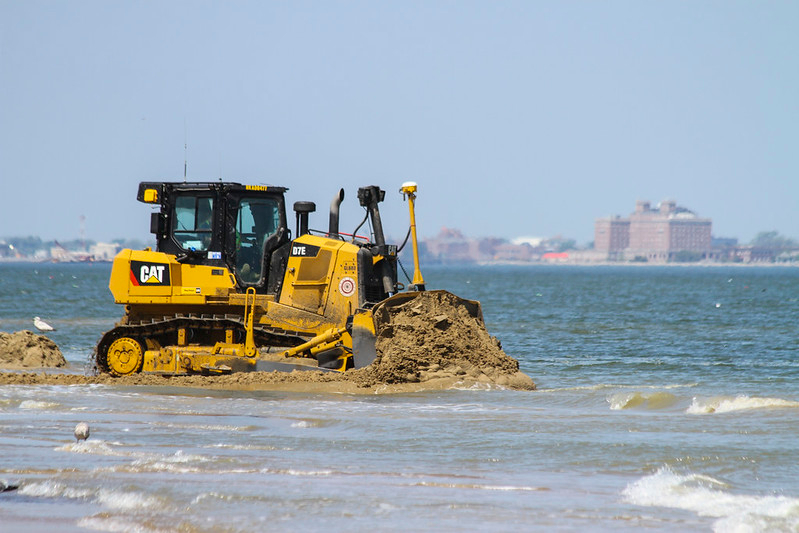

after sand was pumped onshore, bulldozers spread it to create a wider beach at Ocean View
Source: US Army Corps of Engineers, 170428-A-OI229_8
Not all sand dredged from shipping channels ends up being suitable for beach replenishment projects. In 2025, sand excavated from the deepening of the Atlantic Ocean Channel was deposited between 16th and 21st streets at Virginia Beach. The sand grains were then determined to be too small, so the $20 million project was halted before reaching 45th street. However, the same source was judged to be appropriate for a replenishment project at Croatan Beach south of Rudee Inlet; the resort area had higher standards.
The interruption of the replenishment project, leaving a narrow beach, impacted planning for 2026 summer concerts and sports tournaments that attract tourists who rent hotel rooms and generate substantial tax revenue for the city. The three day sand soccer tournament attracted 100,000 people, over 75% from out of town, but it required the most space to create 65 fields between 5th-34th streets. In 2026, the beach was 30 feet narrower so the size of the fields was reduced.6
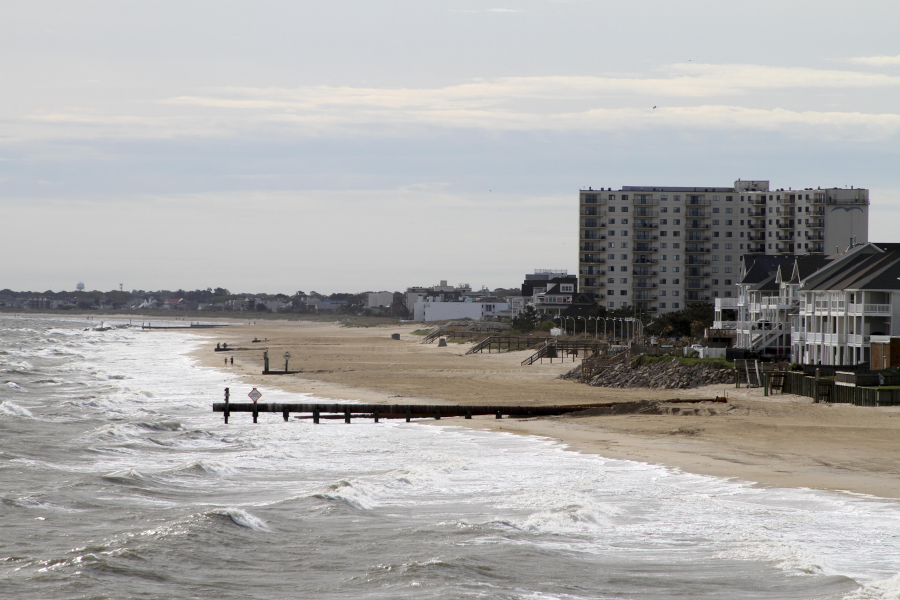

keeping Ocean View Beach 60' wide will require pumping more sand onto the beach every nine years
Source: US Army Corps of Engineers, Norfolk District Image Gallery
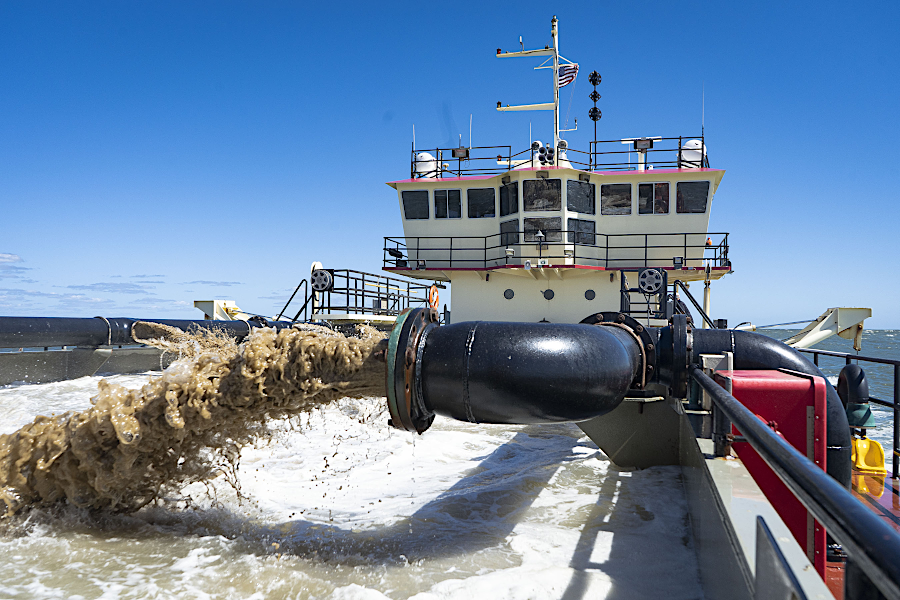
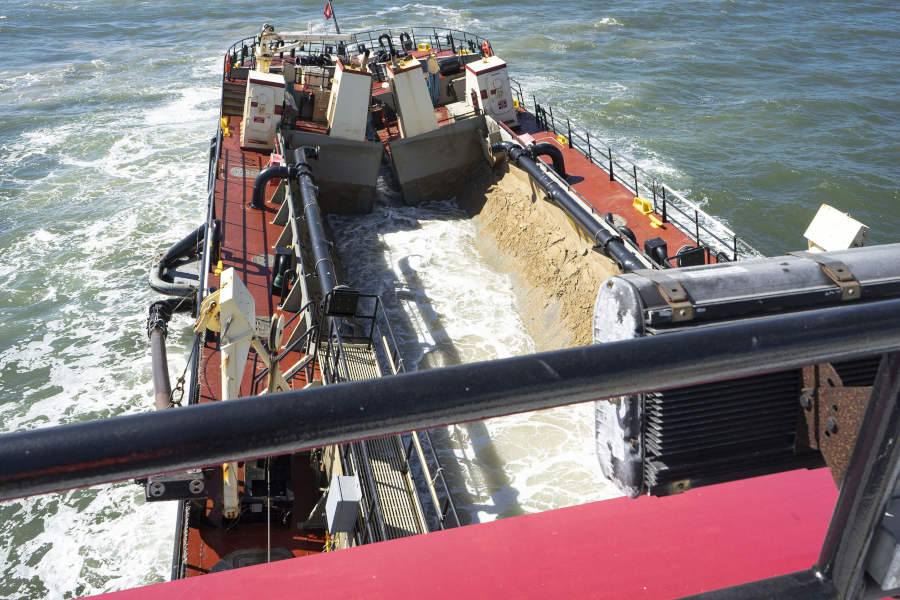
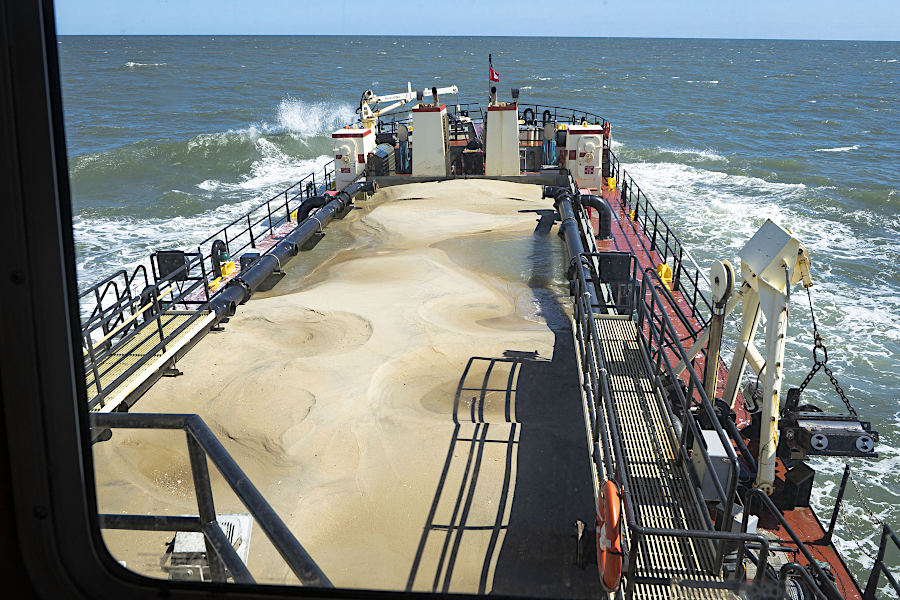



sand can be dredged from shipping channels into barges and then transported to replenish a beach
Source: US Army Corps of Engineers, Army Corps of Engineers districts revitalize Ocean City inlet
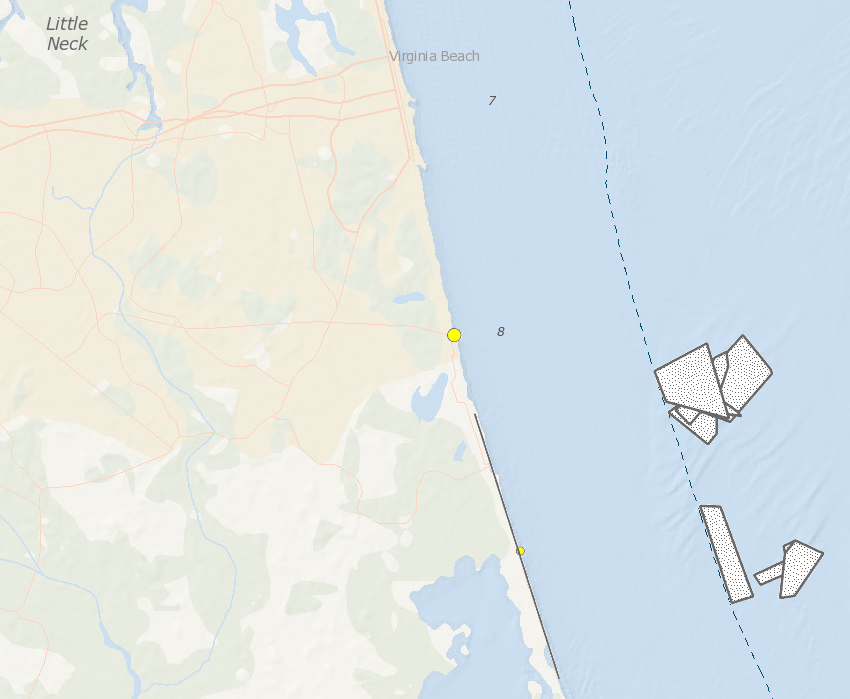
sand dredged from Federal lease areas off Virginia Beach has been used for beach replenishment projects between Sandbridge and the resort area
Source: Bureau of Ocean Energy Management (BOEM), Marine Minerals Information System
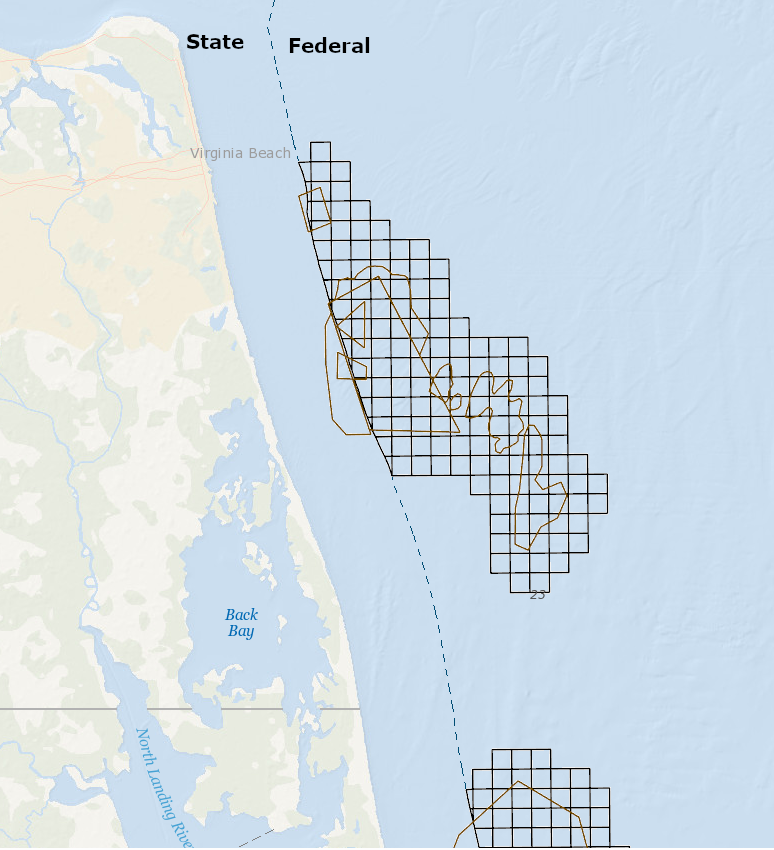
sand resources (brown lines) are both inside and outside the Submerged Lands Act Boundary, but Federal lease areas (black squares) must be at least three miles offshore
Source: Bureau of Ocean Energy Management (BOEM), Marine Minerals Information System
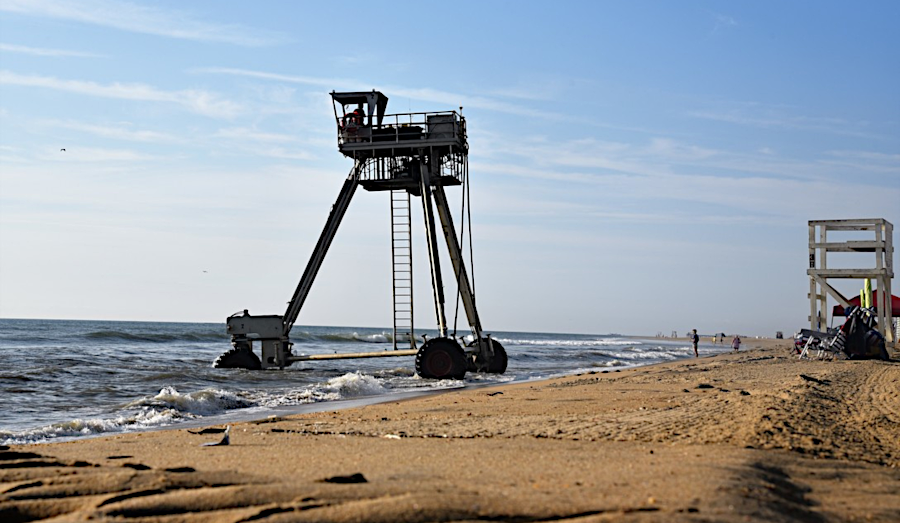

coastal research amphibious buggy conducting survey operations for dredging in the Virginia Beach Hurricane and Storm Damage Reduction Project
Source: US Army Corps of Engineers, Virginia Beach oceanfront continues to grow with help of city, district
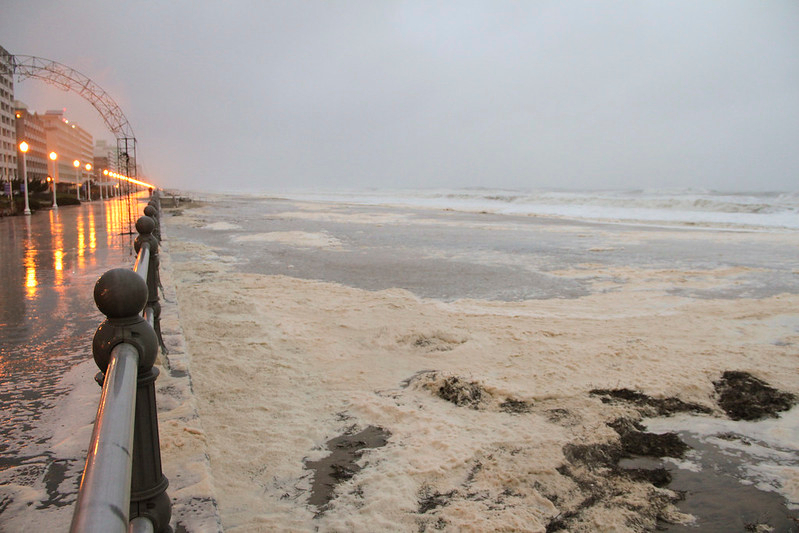

Hurricane Sandy brought waves to the seawall in the resort area of Virginia Beach on October 29, 2012
Source: US Army Corps of Engineers, 121029-A-OI229-006
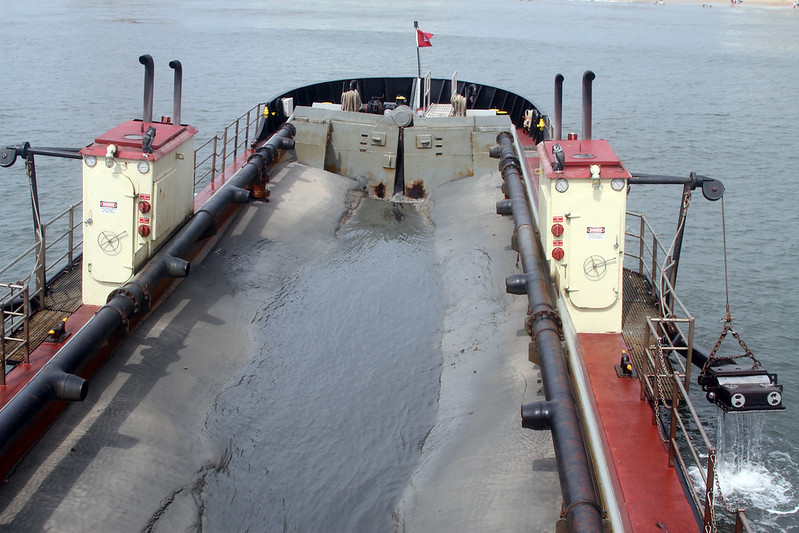

sand is pumped into hopper dredge ships for transport to replenishment sites
Source: US Army Corps of Engineers, Rudee Inlet Dredging
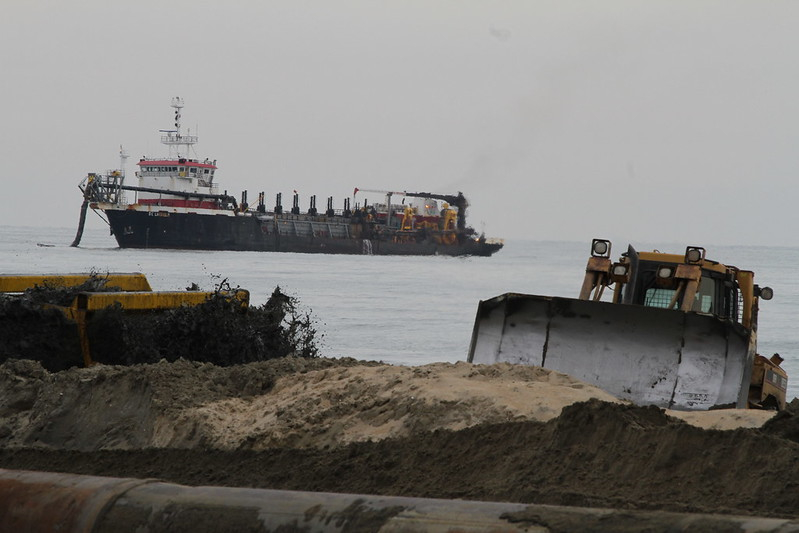

sand for the 2013 Virginia Beach Hurricane Protection Beach Renourishment Project (Big Beach) was brought by a hopper dredge navigational channels north of Cape Henry
Source: US Army Corps of Engineers, 130110-A-ON889-144
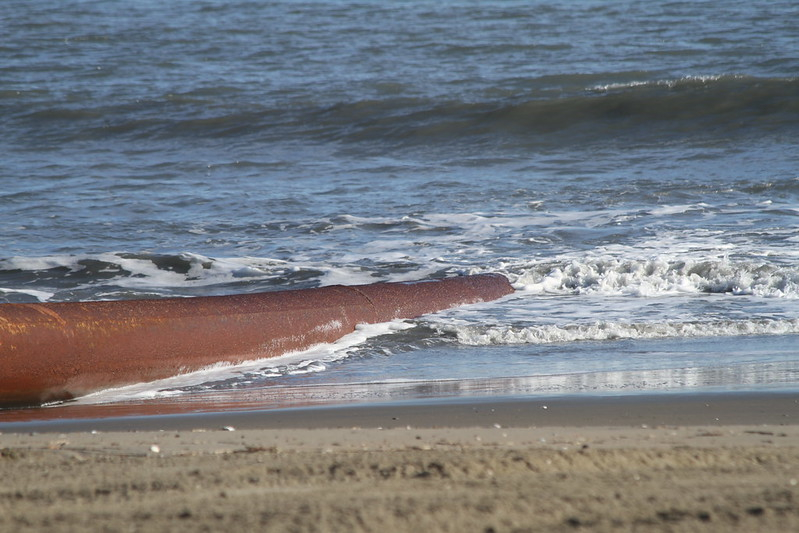

sand was pumped from the hopper dredge though pipes to the resort area beach
Source: US Army Corps of Engineers, 130201-A-ON889-008
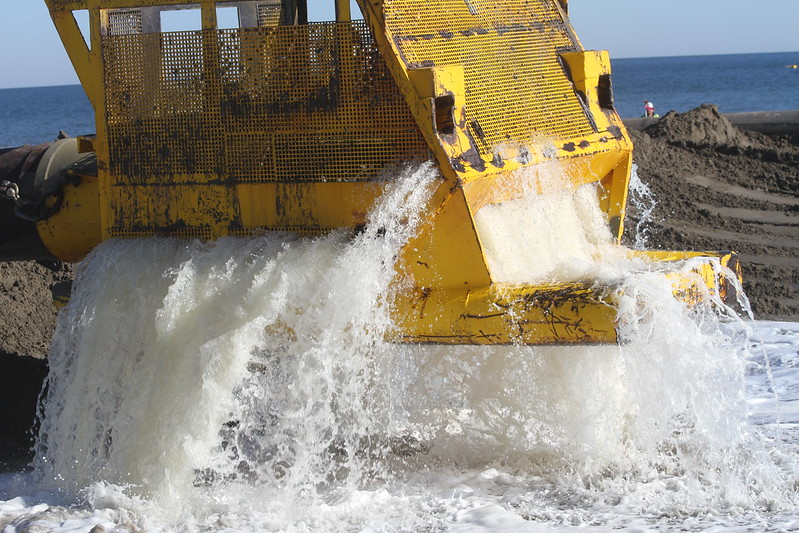

sand and water arrive via the pipe at the beach
Source: US Army Corps of Engineers, 130110-A-ON889-124
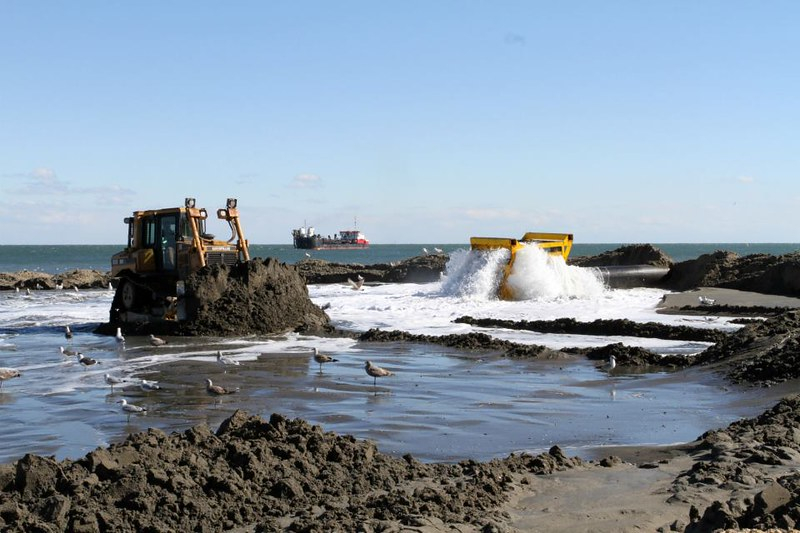

bulldozers spread the sand as it arrives on the beach
Source: US Army Corps of Engineers, 130125-A-ON889-031
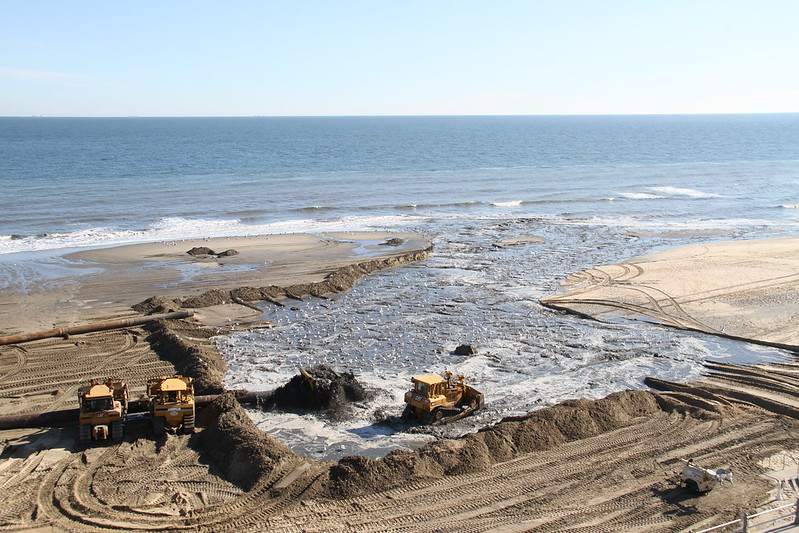

the Big Beach finished with a minimum elevation of 8.5 feet at the seawall
Source: US Army Corps of Engineers, 130110-A-ON889-168
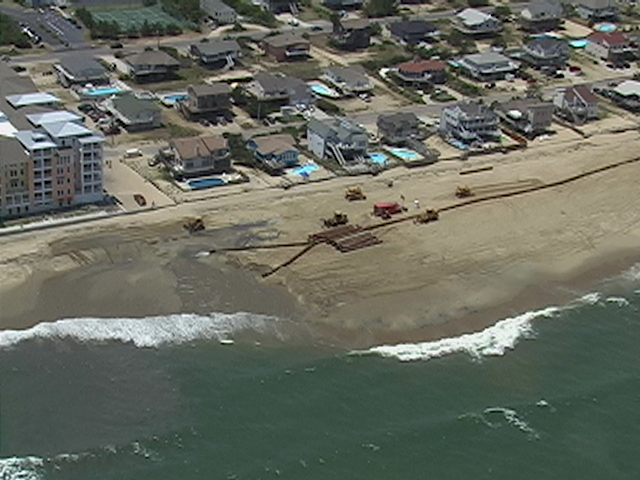

beach replenishment at Sandbridge in 2007
Source: US Army Corps of Engineers, Sandbridge, Va. (070703-A-1111A-006)