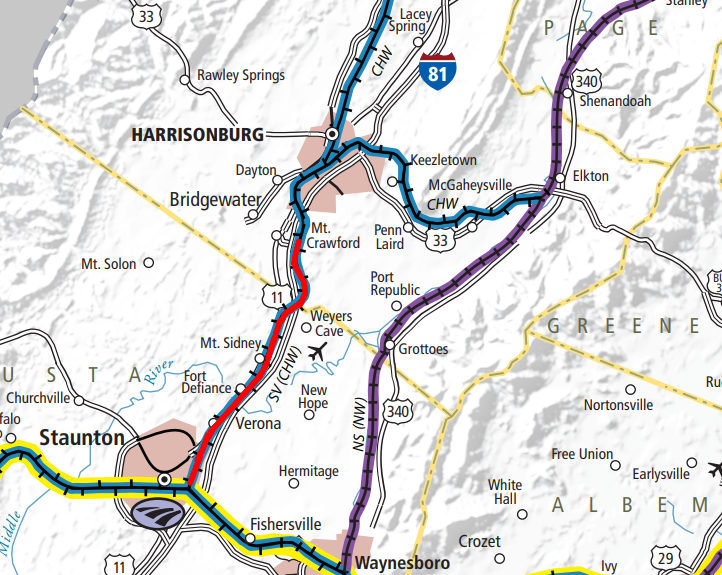
the modern Shenandoah Valley Railroad (red line) runs from Pleasant Valley to Staunton
Source: Virginia Department of Rail and Public Transportation (DRPT), Virginia Rail Map (2012)

the modern Shenandoah Valley Railroad (red line) runs from Pleasant Valley to Staunton
Source: Virginia Department of Rail and Public Transportation (DRPT), Virginia Rail Map (2012)
NOTE: The name "Shenandoah Valley Railroad" has been used for different rail lines west of the Blue Ridge. Identifying the specific railroad using the name requires identifying the date of the reference. The modern Shenandoah Valley Railroad was originally part of the Valley Railroad, constructed in the mid-1800's on the west side of Massanutten Mountain by the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad. The historic Shenandoah Valley Railroad was built in the 1880's through the Page Valley as a competing line. The historic Shenandoah Valley Railroad merged into the Norfolk and Western Railroad, and a segment of the old Valley Railroad is now called the Shenandoah Valley Railroad.
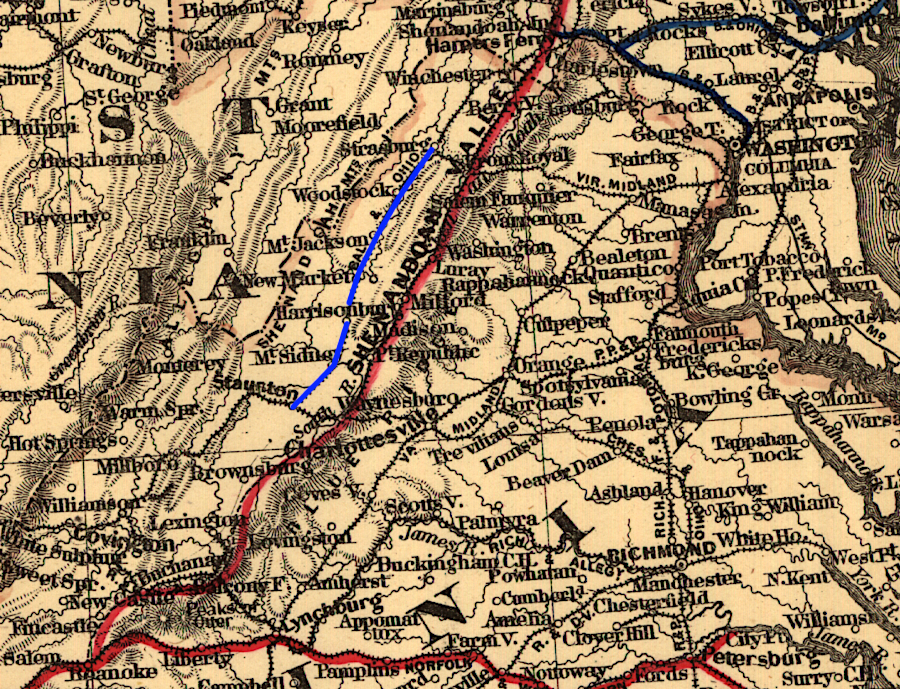
a segment (blue line) of the Valley Railroad in 1881 is now called the Shenandoah Valley Railroad, using the name of a competing 1800's line built east of Massanutten Mountain
Source: Library of Congress, Map showing lines and connections of the Shenandoah Valley and Norfolk & Western Railways (1881)
The modern Shenandoah Valley Railroad connects Pleasant Valley (south of Harrisonburg) and Staunton. It is a 20-mile "short line" railroad, dedicated to moving local agricultural traffic (primarily corn and soybeans) in the valley to connect with the Norfolk Southern at the north end (Pleasant Valley). In Staunton, the short line connects with the Buckingham Branch Railroad and through it with the CSX.
Local shippers along the route of the Shenandoah Valley Railroad are primarily moving corn, soybeans, and other agricultural products. They have the option of using either major carrier.1

the modern Shenandoah Valley Railroad runs on the route established originally by the historic Valley Railroad
Source: Wikipedia, Shenandoah Valley Railroad (short-line)
Today's Shenandoah Valley Railroad is a former part of the Valley Railroad which was built after the Civil War. The historic Valley Railroad was financed largely by the Baltimore and Ohio (B&O) Railroad, in an effort to extend its network to Bristol by connecting with the Virginia and Tennessee Railroad. A rival line on the eastern edge of the Shenandoah Valley, called the Shenandoah Valley Railroad in 1881, was financed initially by the Pennsylvania Railroad.
Though the Valley Railroad had planned to build south from Lexington to Salem, rails were never laid on the incomplete trackbed. It lost a race with the original Shenandoah Valley Railroad. That rival line was built on the western edge of the blue ridge, on the opposite side of Massanutten Mountain from the historic Valley Railroad. The original Shenandoah Valley Railroad connected to the Virginia and Tennessee Railroad near Salem, at a junction which became Roanoke, in 1882. The Shenandoah Valley Railroad then became part of the Norfolk and Western Railroad.
The rival Baltimore and Ohio Railroad lacked the financial capacity to build the planned extension of the historic Valley Railroad south to Salem. Construction was slow, and the race was lost. The original Shenandoah Valley Railroad reached Roanoke/Salem first, and then merged with the Virginia and Tennesee Railroad. Combined and renamed the Norfolk as Western Railroad, it captured most of the traffic generated in the Valley of Virginia.
However, railcars loaded in Staunton and on the western side of Massanutten Mountain could go north past Harrisonburg and Strasburg to the mainline of the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad. That provided some competition to the Norfolk and Western Railroad. By 1896, the Chesapeake & Western Railroad had built 26 miles of track running east-west between Harrisonburg and Elkton, connecting the two rival major north-south railroads.
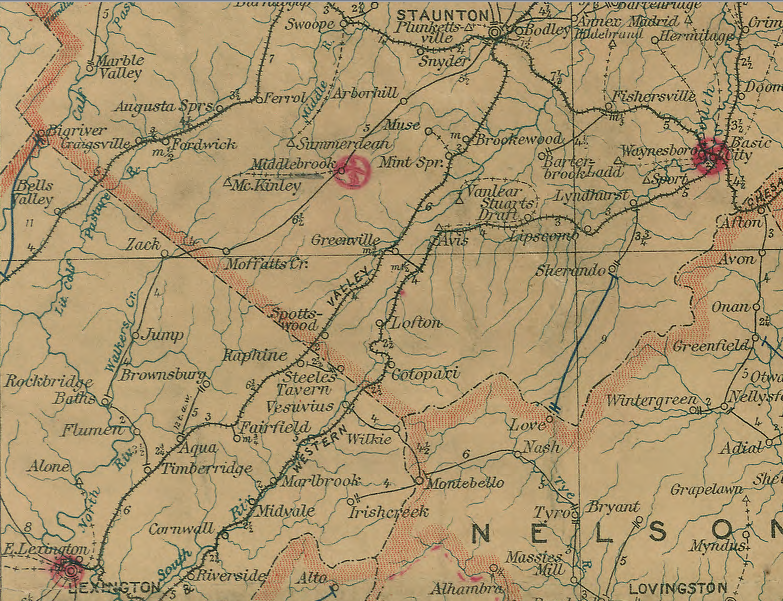
the Valley Railroad connected to Lexington, but construction stopped there
Source: Library of Congress, Post route map of the states of Virginia and West Virginia (Postmaster General, 1906)
In 1942, the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad sold that part of the Valley Branch which connected Lexington to Harrisonburg. The Chesapeake & Western Railroad purchased the track. It pulled up the rails between Lexington and Staunton, but kept the northern section intact. The Chesapeake & Western Railroad ran trains from its connection with the Chesapeake and Ohio Railroad at Staunton north to Harrisonburg. At Harrisonburg, trains used Chesapeake & Western Railroad to go east across the valley and interchange at Elkton with the Norfolk and Western Railway.
The Norfolk and Western Railway had begun to finance the Chesapeake & Western Railroad in 1938. It acquired control in 1954, but chose to retain the Chesapeake & Western Railroad name. The Norfolk and Western Railway merged with the Southern Railway to create the Norfolk Southern in 1982.
The Norfolk Southern stopped operating trains on the rails south of Pleasant Valley in 1985. Trains stopped going west of Pleasant Valley in 1987. In 1993, Norfolk Southern sold the southern portion of the Chesapeake & Western Railroad track, going south from Pleasant Valley to Staunton. Local investors purchased that track in order to maintain rail service to local industries.
The investors chose to name their new short line railroad the Shenandoah Valley Railroad. The did not choose to honor the original Valley Railroad that built the tracks south of Harrisonburg. Instead, they chose to honor the rival line that built the original tracks on the eastern side of Massanutten Mountain.2
Today, a private consortium owns the track between Pleasant Valley (south of Harrisonburg) and Staunton. One of the owners, Houff Corporation, has a transloading facility in Weyers Cave that facilitates transfer of products between trucks and trains. In 2020, another local warehousing firm, the InterChange Group, also acquired an interest in the Shenandoah Valley Railroad after opening a new cold-storage facility with a rail spur.3
At Staunton, the Shenandoah Valley Railroad now interchanges with the Buckingham Branch Railroad. Trains are operated by the Durbin & Greenbrier Valley Railroad, which also manages operations on the West Virginia’s Cass Scenic Railroad in West Virginia. The three Shenandoah Valley Railroad locomotives are based in Staunton. Typically two are used, five days a week, to switch cars from freight customers and carry them to interchange with the Norfolk Southern or the Buckingham Branch Railroad.4
In 2020, the Friends of the Shenandoah Rail Trail organized (initially as the Shenandoah Rail Trail Exploratory Partnership, with support from the Alliance for the Shenandoah Valley) and proposed to convert the 49-mile stretch of "out of service" track into a bike/pedestrian trail passsing through Rockingham, Shenandoah, and Warren counties. At the direction of the General Assembly, the Virginia Department of Conservation and Recreation completed a "Feasibility Study for a Linear Park in the Shenandoah Valley" in 2021.
The study concluded that a 10-foot wide asphalt trail with 2-foot wide shoulders was feasible. Costs were projected to be $90-120 million, or $1.1 to $1.3 million per mile. 5
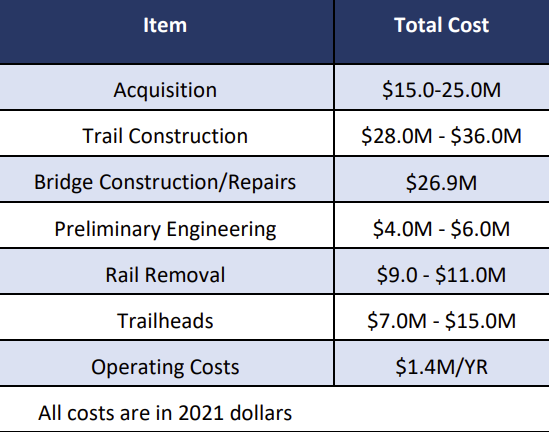
total costs to build the 49-mile long Shenandoah Rail Trail were projected in 2021 to be $90-120 million
Source: Virginia Department of Conservation and Recreation, Feasibility Study for a Linear Park in the Shenandoah Valley (p.9)
The non-government organization obtained resolutions of support from the elected officials of all nine towns and three counties along the route. It also held 10 community meetings in 2023 to explain the proposal to local residents.
Norfolk Southern agreed to sell the route, since the company had been unable to get the modern Shenandoah Valley Railroad or any other short line railroad to buy it. The 2023 the General Assembly appropriated $35 million for the project. The legislature also allocated money for four other rail-to-trail projects - the Craig Valley Trail, Peaks to Creeks Trail, Tobacco Heritage Trail, and Eastern Shore Rail Trail. Even though delegates and state senators from Northern Virginia districts held key positions in the General Assembly, no special funding was allocated to that region in 2023. There were no rails-to-trails proposals in Northern Virginia.
The Friends of the Shenandoah Rail Trail planned to "rail bank" the old Valley Railroad corridor from Broadway to Front Royal. That approach, overseen by the Surface Transportation Board, would preserve the potential for reinstalling track for rail service if freight or passenger demand increased in the future. The mayor of Edinburg said:6
Houff Corporation has a transloading facility on the Shenandoah Valley Railroad
Source: ESRI, ArcGIS Online