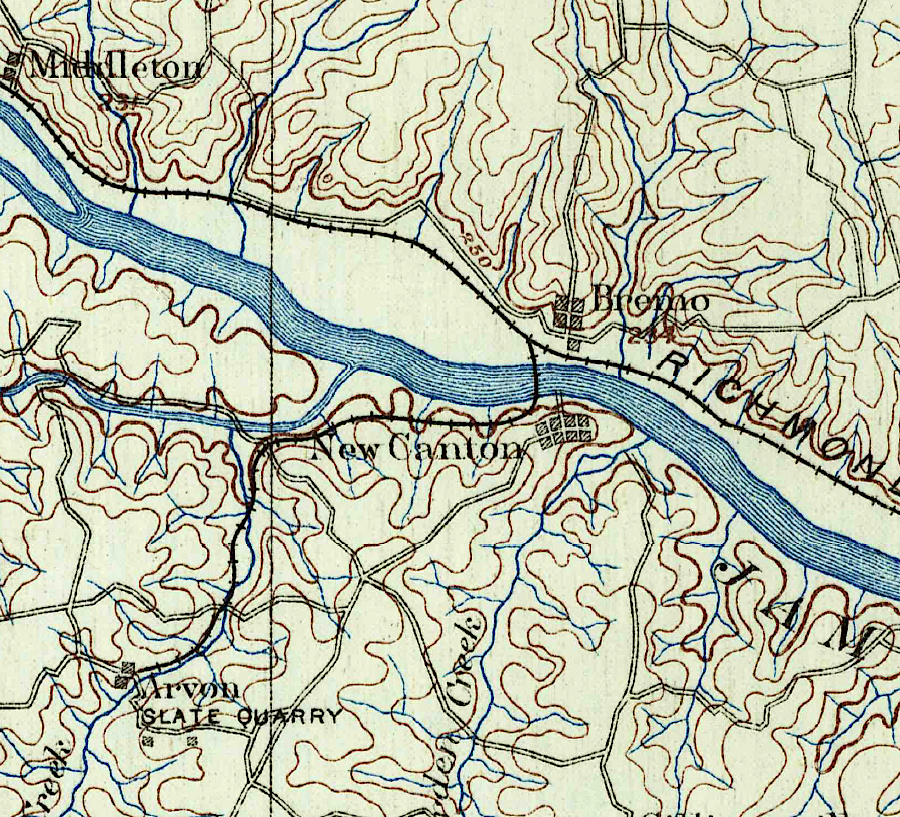
the Buckingham Railroad was built primarily to haul slate to Richmond
Source: US Geological Survey (USGS), Palmyra VA 1:125,000 topographic quadrangle (1891)

the Buckingham Railroad was built primarily to haul slate to Richmond
Source: US Geological Survey (USGS), Palmyra VA 1:125,000 topographic quadrangle (1891)
The Buckingham Branch is a short line railroad that started running trains in 1989 on the 17-mile stretch of track between Dillwyn to Bremo Bluff.
The Buckingham Railroad was chartered on March 3, 1879 to carry state from the quarry at Arvonia to the Richmond & Alleghany Railroad, which had been chartered just a year earlier. The Richmond & Alleghany Railroad completed track on the north side of the James River across from Buckingham County in 1881. However, there was an economic recession in 1880 and the Richmond & Alleghany Railroad went bankrupt in 1883. It would not be until 1885 that the Buckingham Railroad was built, including a bridge across the James River to the Richmond and Alleghany Railroad at Bremo Bluff. The Richmond & Alleghany Railroad leased it.
The Chesapeake and Ohio (C&O) Railway purchased the Richmond and Alleghany in 1889. It extended the branch, ultimately to Rosney almost three miles further south of Dillwyn. Plans to build further south to connect with the Norfolk and Western Railway at Farmville were never implemented.
In 1897, the Chesapeake and Ohio Railway ended the separate corporate status of the Buckingham Railroad, merging it into the C&O.
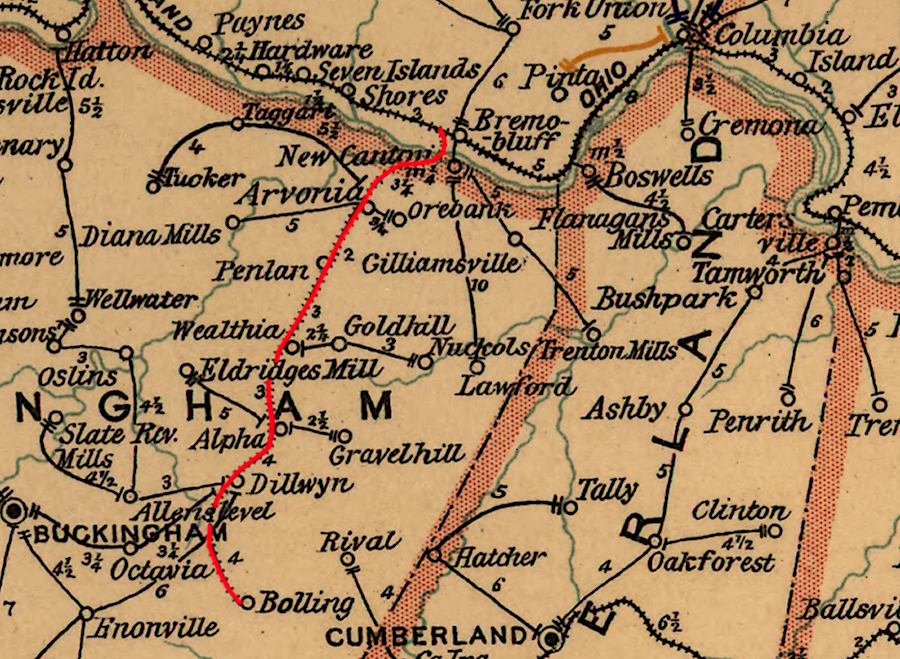
the Buckingham Railroad in 1896, just before it was folded into the Chesapeake and Ohio Railway
Source: Library of Congress, Post route map of the state of Virginia and West Virginia (1896)
The Chesapeake and Ohio (C&O) Railway was folded into CSX in 1987. The track to Dillwyn was deemed surplus and sold to the Buckingham Branch Railroad. It was organized in 1988 by the family of a retiree from the Chesapeake & Ohio Railway, and operations began in 1989. Making the track available to a short line freed CSX of operating expenses, while assuring it of freight traffic brought north to Bremo Bluff.1
The Buckingham Branch Railroad expanded in 2004, acquiring rights to operate on the CSX track between Richmond and Clifton Forge. The Virginia Central had originally constructed most of that track prior to the Civil War; the Chesapeake and Ohio Railroad built the western end later. The Buckingham Branch Railroad now operates the trains that pass though the Blue Ridge Tunnel between Charlottesville and Staunton.
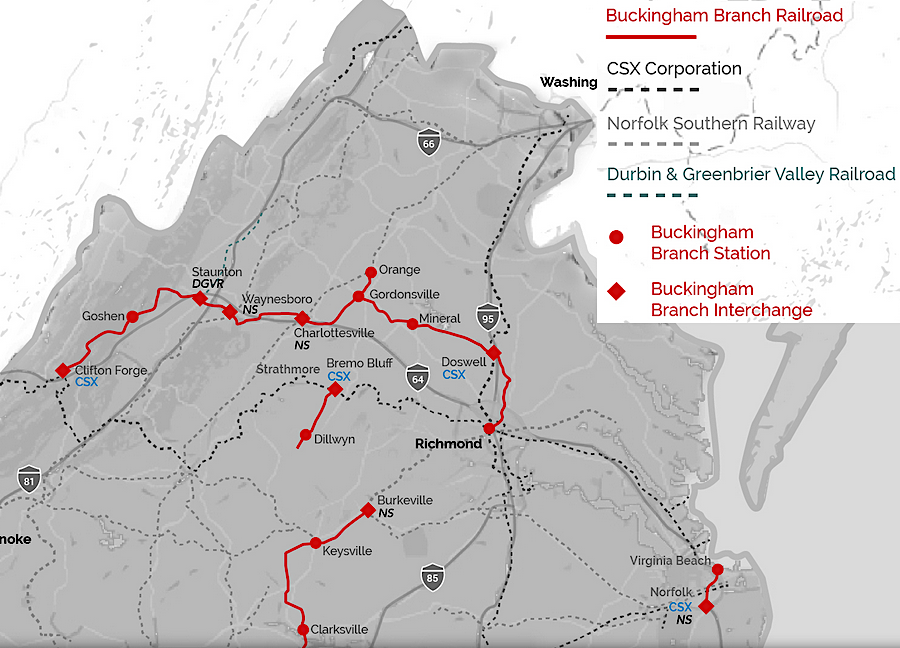
the Buckingham Branch Railroad is the largest short line railroad in Virginia, with over 280 miles of track in four divisions
Source: Buckingham Branch Railroad
CSX continued to send its empty coal trains westward on the Buckingham Branch Railroad, routing loaded coal trains headed to Newport News on the gentler grades of the track running parallel to the James River on the old towpath of the James River and Kanawha Canal. When Governor Northam announced in December, 2019 that the state would purchase the CSX track between Doswell and Clifton Forge, the Virginia Department of Rail and Public Transportation (DRPT) announced that Buckingham Branch Railroad operations over that line would continue.2
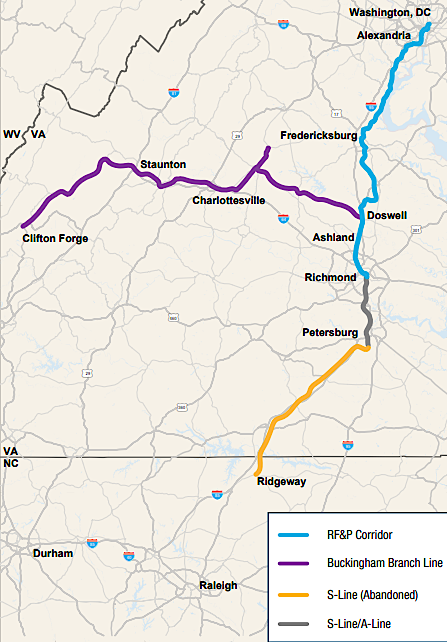
Virginia committed to continued use by the Buckingham Branch Railroad of the Doswell-Clifton Forge track (purple) that the state agreed to purchase in 2019
Source: Virginia Department of Rail and Public Transportation (DRPT), Map of Future Program Highlights
The next expansion was in 2009. The Buckingham Branch Railroad leased the 59 miles of Norfolk Southern track between Burkeville and Clarksville.3
The track between Clarksville and Keysville had been built in 1884 by the Richmond and Mecklenburg Railroad. The track between Keysville and Burkeville had been completed by the Richmond and Danville Railroad, which connected those two cities in 1856. It was operated by the Southern Railway until its merger of the Norfolk and Western Railroad in 1982.
The new Norfolk Southern Railroad reduced costs by abandoning duplicative track, or spinning off short lines to create the Thoroughbred Shortline Program. In 2009, Norfolk Southern changed operators and the Buckingham Branch Railroad began operating the "Virginia Southern" between Clarksville and Keysvville.4
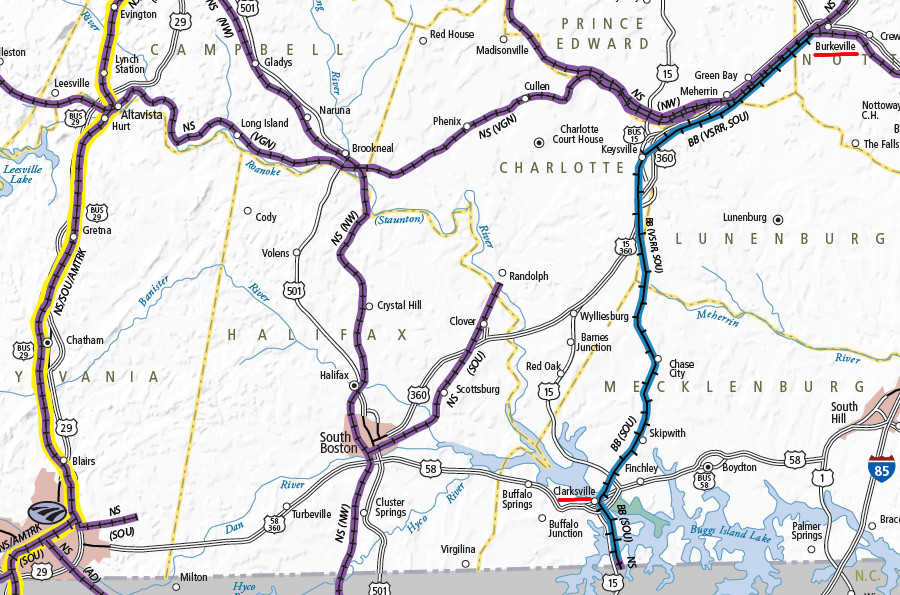
the Buckingham Branch Railroad operates the Virginia Southern shortline between Burkeville and Clarksville
Source: Virginia Department of Rail and Public Transportation (DRPT), Virginia State Rail Map
The most recent expansion, creating the fourth division of the Buckingham Branch Railroad, occurred in 2018. The private corporation owned by Northampton and Accomack counties, Canonie Atlantic Company, shut down the Bay Coast Railroad on the Eastern Shore. That ended the unique car float that barged freight cars across the Chesapeake Bay between Cape Charles (in Northampton County) and Little Creek (in Norfolk, next to Virginia Beach).
Most of the Bay Coast Railroad track on the Eastern Shore was abandoned, but the track at Little Creek retained value. It provided an interconnection between Norfolk Southern's Portlock Yard and the CSX, via traffic rights over the Norfolk Portsmouth Beltline to Coleman Place. It also serviced the Navy's amphibious base at Little Creek, part of Joint Expeditionary Base Little Creek-Fort Story.5
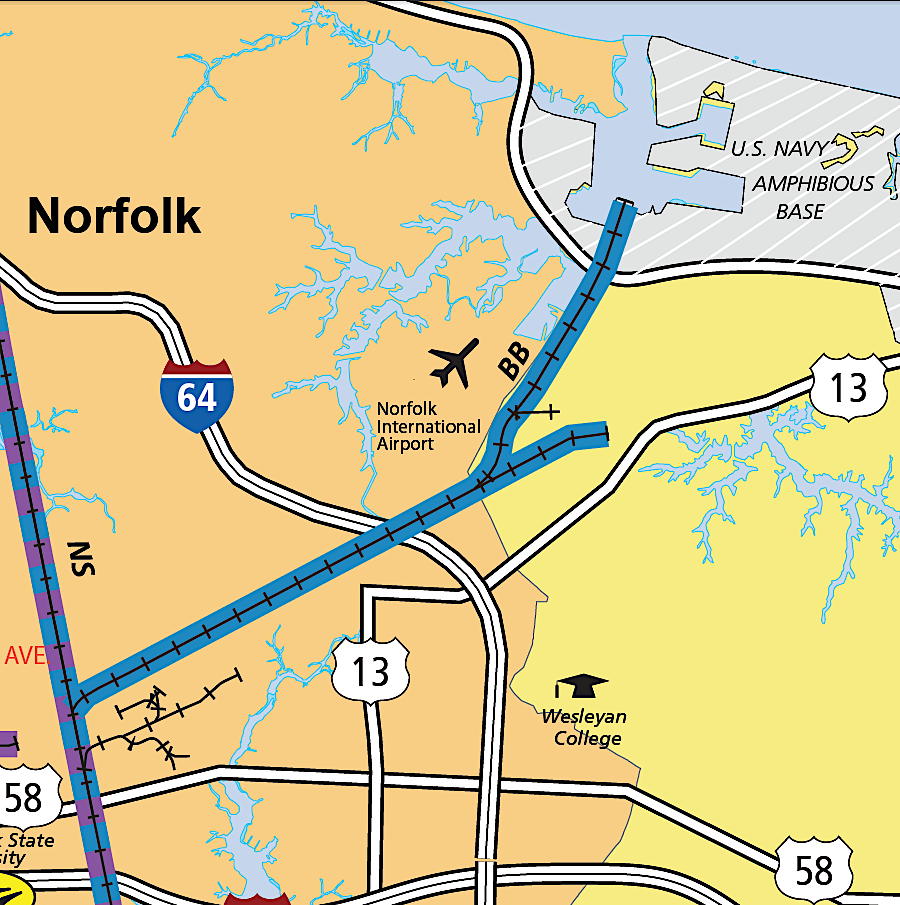
in 2019, the Buckingham Branch took over the track which the Bay Coast Railroad had operated at Little Creek in Virginia Beach/Norfolk
Source: Virginia Department of Rail and Public Transportation, Virginia State Railroad Map (2019)
Today, the Buckingham Branch Railroad advertises:6
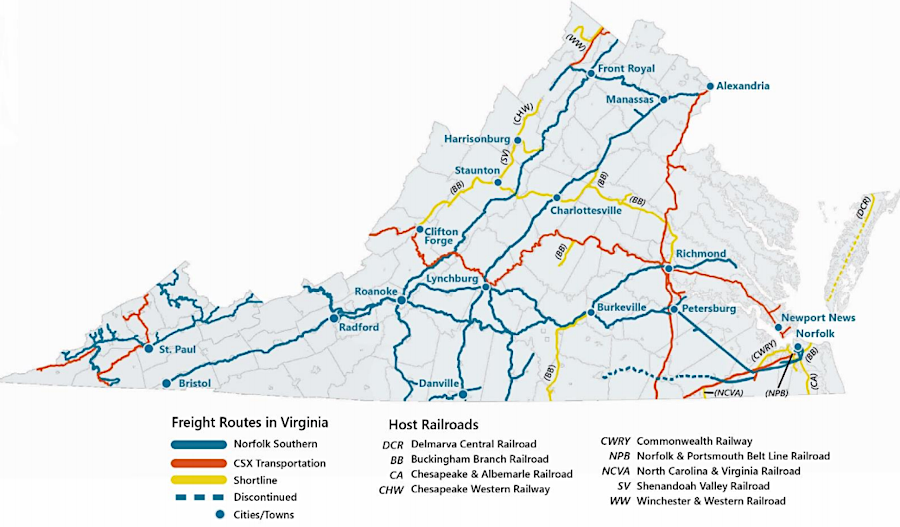
shortlines such as the Buckingham Branch Railroad provide freight rail service to large portions of the state
Source: Virginia Department of Rail and Public Transportation, Virginia's Rail Network (2020)
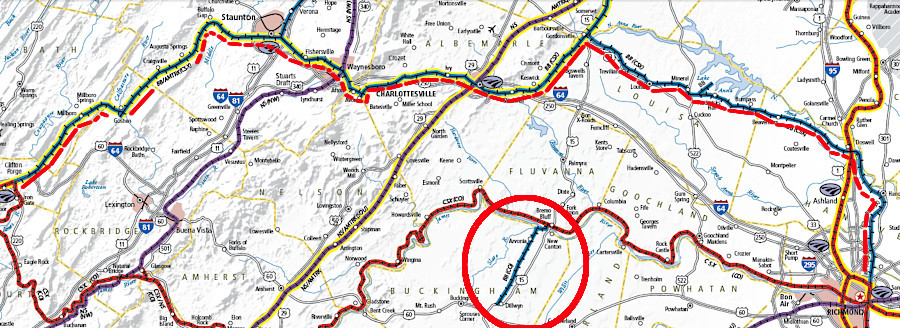
the Buckingham Branch Railroad began operating between Dillwyn-Bremo Bluff (red circle) in 1989, and between Richmond-Clifton Forge in 2004
Source: Virginia Department of Rail and Public Transportation (DRPT), Virginia State Rail Map
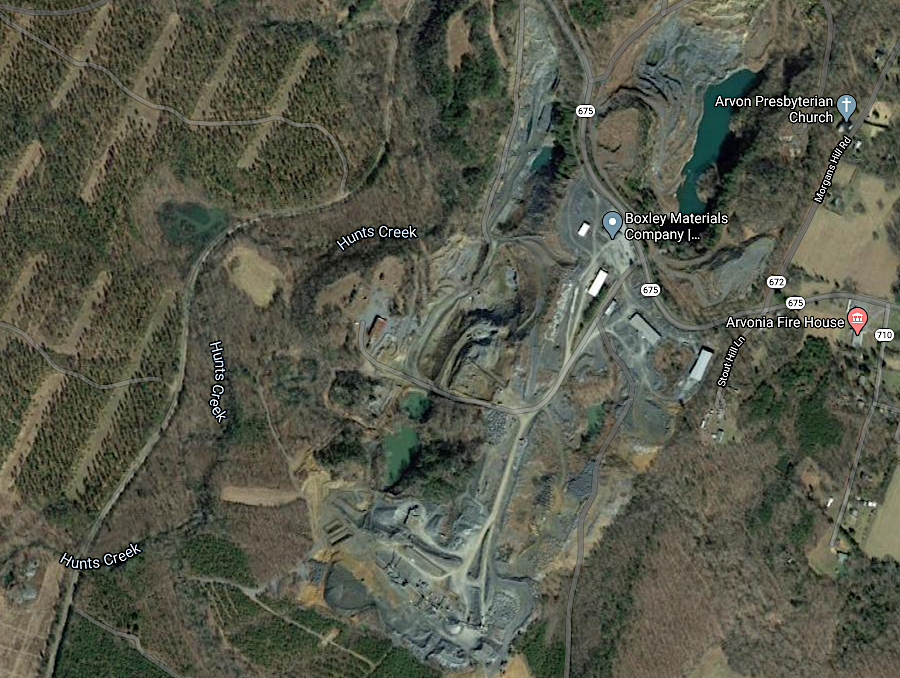

the slate quarry at Arvonia which originally justified construction of the Buckingham Railroad is still active
Source: GoogleMaps
In 2022, the Buckingham Branch Railroad opened the Virginia Scenic Railway to offer excursion trips from the train station in Staunton. The Blue Ridge Flyer traveled east, going though the Blue Ridge Tunnel that was opened in 1944 before turning around in Ivy and returning to Staunton. The Alleghany Special traveled west from Staunton, turning around at Goshen in Rockbridge County. Trains went 25-30mph, and had to give the right-of-way to CSX freight and Amtrak passenger trains.1 "All Aboard the Virginia Scenic Railway," Virginia Scenic Railway, https://www.virginiascenicrailway.com/ (last checked July 24, 2022)

Buckingham Branch Railroad office in Dilwyn (Buckingham County)