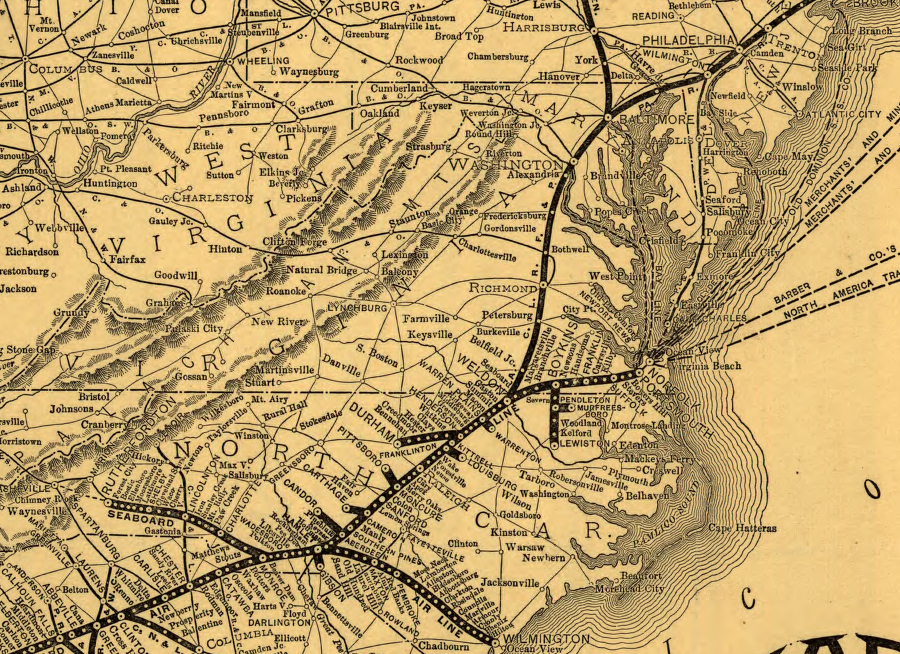
in 1896, the Seaboard Air Line relied upon the Atlantic Coast Line to go north from Weldon
Source: Library of Congress, Map of the Seaboard Air Line and its principal connections north, south, east & west, 1896 (Rand McNally and Company)

in 1896, the Seaboard Air Line relied upon the Atlantic Coast Line to go north from Weldon
Source: Library of Congress, Map of the Seaboard Air Line and its principal connections north, south, east & west, 1896 (Rand McNally and Company)
The Seaboard & Roanoke Railroad acquired control of the Raleigh and Gaston Railroad and the Raleigh & Augusta Air Line Railroad. By 1881 their operations, on track that stretched from the South Carolina border to Portsmouth, were synchronized and marketed as the Seaboard Air-Line. Other railroads also joined in advertising coordinated service, including the Roanoke & Tar River Railroad, suggesting the "air line" offered a fast route as straight as a crow would fly.
The Richmond and Danville Railroad and the Richmond and West Point Terminal Railway and Warehouse Company demonstrated in the 1880's how a holding company could consolidate both financial ownership and daily operations of multiple railroads. Synchronization of advertising, billing, and train movements streamlined transport of long-distance freight and passengers, generating more revenue and higher profits.
Though "the Terminal" had collapsed after the financial recession starting in 1894, the Southern Railway emerged as a large system in 1894. The Southern Railway's trunk line ran inland, parallel to the Blue Ridge between Alexandria to Atlanta. The Seaboard Air Line developed as a competitive route between Atlanta and the Chesapeake Bay wharves at Portsmouth.
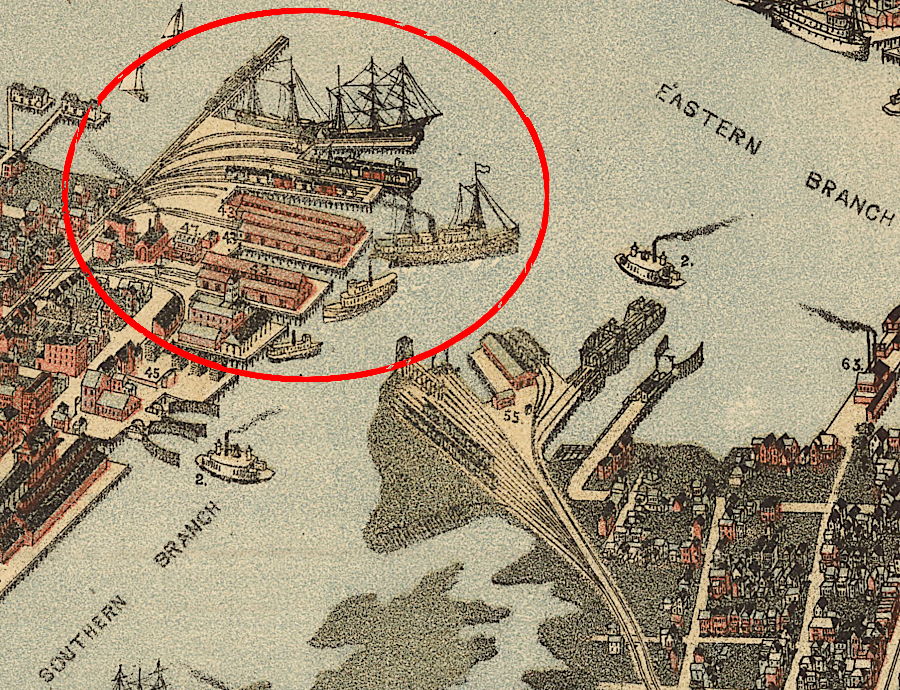
the Seaboard Air Line depot at Portsmouth in 1891, across the Southern Branch from the original Norfolk Southern Railroad in Berkley
Source: Library of Congress, Bird's eye view of Norfolk, Portsmouth and Berkley, Norfolk Co., Va (1891?)
In 1898, the Seaboard Air Line controlled 915 miles of track. In 1899, it controlled 2,353 miles.
Service from Portsmouth to Atlanta was expanded to Florida, converting the railroad into a north-south operation from Richmond to Tampa. Freight include produce and phosphate from Florida, and passenger service was a major priority. The Orange Blossom Special carried northern passengers to Miami on a winter-only luxury train. Later named trains, the Meteor and Star, are still operated by Amtrak today.
A corporate reorganization led by John Skelton Williams officialy created the Seaboard Air Line Railway in 1900 as a single corporation. In 1930, at the start of the Great Depression, the Seaboard Air Line Railway went into bankruptcy. A 1946 reorganization changed the corporate name to Seaboard Air Line Railroad.1
"North Carolina Railroads - Raleigh & Gaston Railroad," Carolana, http://www.carolana.com/NC/Transportation/railroads/nc_rrs_raleigh_gaston.html; "North Carolina Railroads - Seaboard Air Line Railway / Railroad," Carolana, http://www.carolana.com/NC/Transportation/railroads/nc_rrs_seaboard_air_line.html; Fairfax Harrison, A History of the Legal Development of the Railroad System of Southern Railway Company, 1901, p.21, https://books.google.com/books?id=0IkjAQAAMAAJ; "Remembering the Seaboard Air Line Railroad," Classic Trains, March 1, 2021, https://www.trains.com/ctr/railroads/fallen-flags/remembering-the-seaboard-air-line-railroad/ (last checked October 9, 2021)
One inland competitor to the Seaboard Air Line was the Piedmont Air Line, running parallel to the Blue Ridge. The Richmond & Danville Railroad partnered with other lines in North Carolina and Georgia to advertise a coordinated route between Richmond and Atlanta. The Southern Railway maintained the marketing after acquiring control of the railroads operating that inland route in 1894. The other main competitor was the Atlantic Coast Line, following the Fall Line.2
"Piedmont Air-Line," RailGa.com, https://railga.com/piedmont.html (last checked January 17, 2019)
Organizing multiple railroads to offer through freight service was a challenge. After John Robinson died in 1893, John Skelton Williams became the primary leader of the effort. He was willing to bargain hard.
Richmond was the northern limit of the Seaboard Air Line. Until 1900, the Atlantic Coast Line was unwilling to offer acceptable rates for forwarding freight from the Seaboard Air Line north to Washington DC. The Atlantic Coast Line controlled the Richmond, Fredericksburg and Potomac (RF&P) Railroad, and the charter for that line gave it a monopoly between Richmond and Washington.
However, the General Assembly had the authority to pass new legislation that was inconsistent with the old charter. John Skelton Williams lobbied effectively, and in 1900 the legislature authorized construction of a competing railroad parallel to the Richmond, Fredericksburg and Potomac Railroad. The Atlantic Coast Line quickly concluded negotiations with the Seaboard Air Line to forward freight, and no second railroad was constructed.3 Jim Cox, https://books.google.com/books?id=gY4FgCKdb7UC, McFarland, 2010, pp.171-173, https://books.google.com/books?id=gY4FgCKdb7UC (last checked January 25, 2019)
Completion of the Richmond, Petersburg & Carolina Railroad in 1900 allowed the Seaboard Air Line to avoid using the rival Atlantic Coast Line track between Weldon and Richmond. North of the James River, the Seaboard Air Line and the Chesapeake and Ohio Railway partnered to build Main Street Station.
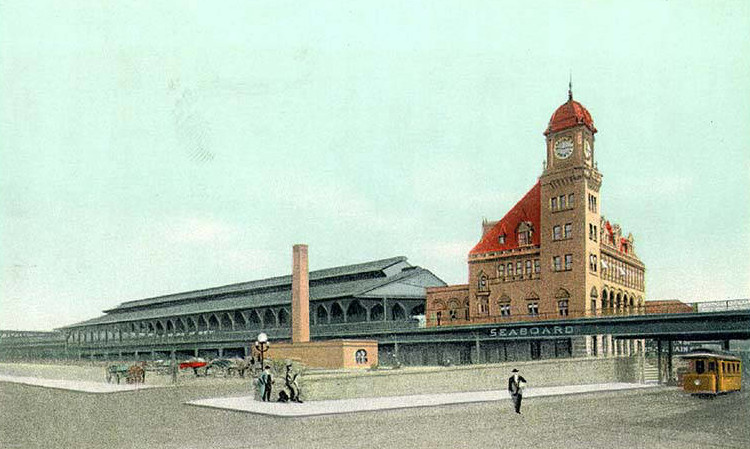

in 1901, the Seaboard Air Line and Chesapeake and Ohio Railway opened Main Street Station in Richmond
Source: Virginia Commonwealth University (VCU), Main Street Station, Richmond
They also worked together to built viaducts to cross over the Southern Railway track on the ground in 1900-1901. The resulting interchange of railroads created the Triple Crossing. The Triple Crossing was a unique railroad feature until the Kansas City Terminal Railway created the Sante Fe Junction in Kansas City, and construction of the flood wall along the James River moved the ground-level track slightly.3
"Kansas City, MO: Triple Crossing of railroad tracks (Santa Fe Junction)," Towns and Nature, June 22, 2019, 3
"Railroading on Three Levels," Southern Railfan, http://southern.railfan.net/ties/1950/50-4/three.html; "Triple Crossing," American-Rails.com, https://www.american-rails.com/triple-crossing.html (last checked July 5, 2020)
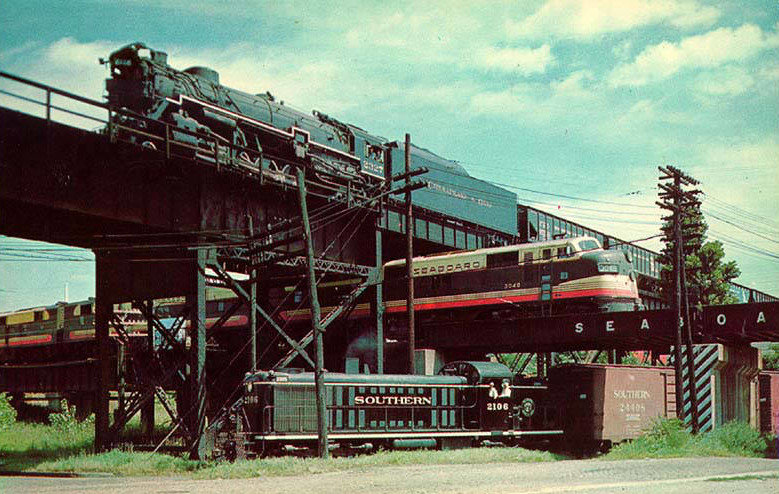

the Seaboard Air Line occupied the middle level of the Triple Crossing in Richmond
Source: Virginia Commonwealth University (VCU), Is Two over One Railroad Fare? (1949)
The connection at Norlina was the third time a Virginia railroad had built a connection to the railroad network in North Carolina.
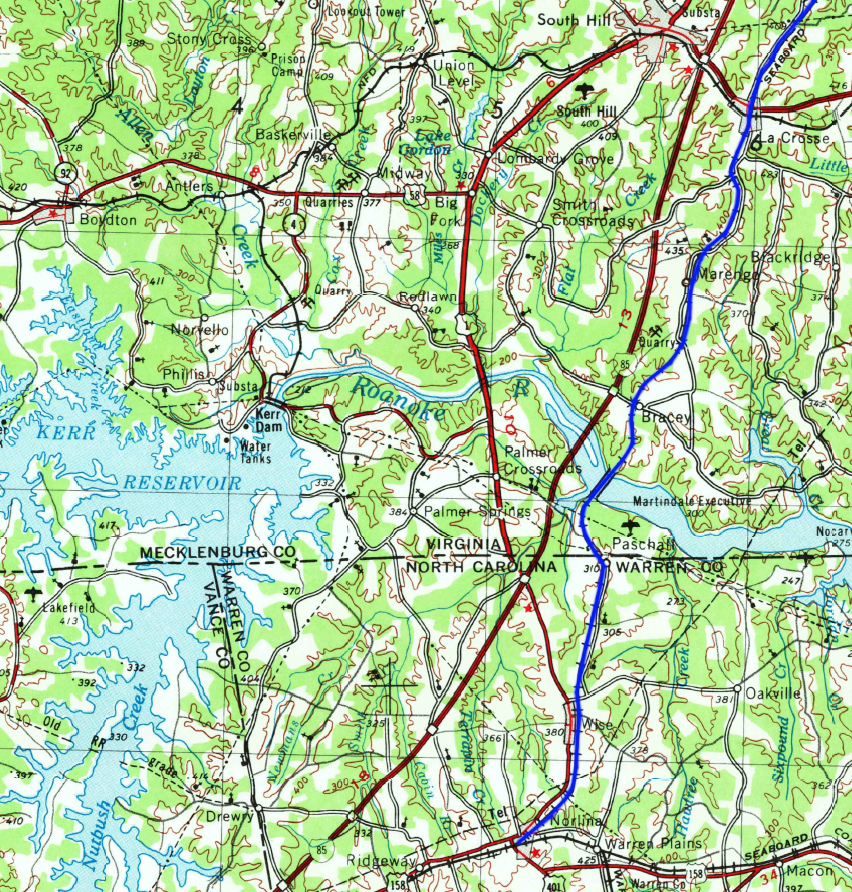
the Seaboard Air Line connected to the original Raleigh and Gaston Railroad route at what became Norlina
Source: US Geological Survey (USGS), Greensboro NC 1:250,000 scale topographic quadrangle (1953)
Prior to the Civil War, the Roanoke Railroad linked Clarksville to the North Carolina railroad at Manson, allowing tobacco to be shipped by rail rather than batteaux or wagon. After the Civil War, the Oxford and Clarksville Railroad chose to connect to the North Carolina Railroad at Oxford. That connection offered a through route to Richmond, via the Richmond and Mecklenburg Railroad north from Clarksville to Keysville and then the Richmond and Danville Railroad.
The Richmond, Petersburg & Carolina Railroad connected at Ridgeway Junction, which renamed itself Norlina in 1913. That location provided a straight path to Petersburg. 3
"Home," Town of Norlina, http://norlinanc.com/ (last checked June 30, 2020)
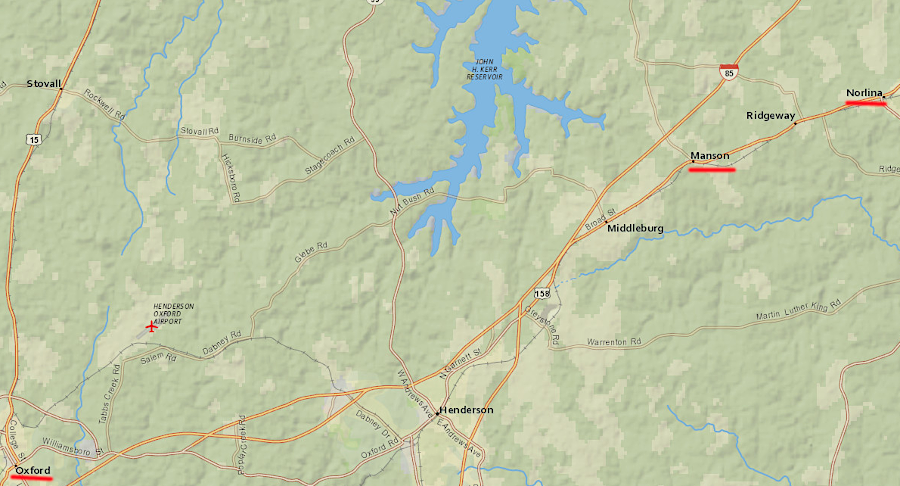
Virginia railroads connected to the route of the original Raleigh and Gaston Railroad at three places south of Clarksville
Source: ESRI, ArcGIS Online
The Seaboard Air Line replaced its coal-fired steam engines with diesels by 1953.3
"Remembering the Seaboard Air Line Railroad," Classic Trains, March 1, 2021, https://www.trains.com/ctr/railroads/fallen-flags/remembering-the-seaboard-air-line-railroad/ (last checked October 9, 2021)
The Seaboard Air Line and the Atlantic Coast Line began merger discussions in 1958. They reached agreement in 1963, but lawsuits delayed the merger until 1967. The nine years of negotiations started as the Interstate Commerce Commission (ICC) began authorizing significant mergers with approval of the Norfolk and Western Railway's acquisition of the Virginian Railway. The merger of those two rivals in 1959 led to a wave of railroad consolidations, ultimately leaving just two Class I railroads in Virginia.
The Seaboard Coast Line partnered with the Louisville & Nashville Railroad, Clinchfield Railroad, and others in Georgia and Alabama in 1974 as the "Family Lines System." They shared billing and advertising, but were not merged together until creation of the Seaboard System Railroad at the end on 1982. That corporate entity lasted until it was folded into CSX Transportation in 1986.3
"CSX merger family tree," Trains, June 2, 2006, https://trn.trains.com/railroads/railroad-history/2006/06/csx-merger-family-tree; "Remembering the Seaboard Air Line Railroad," Classic Trains, March 1, 2021, https://www.trains.com/ctr/railroads/fallen-flags/remembering-the-seaboard-air-line-railroad/ (last checked October 9, 2021)
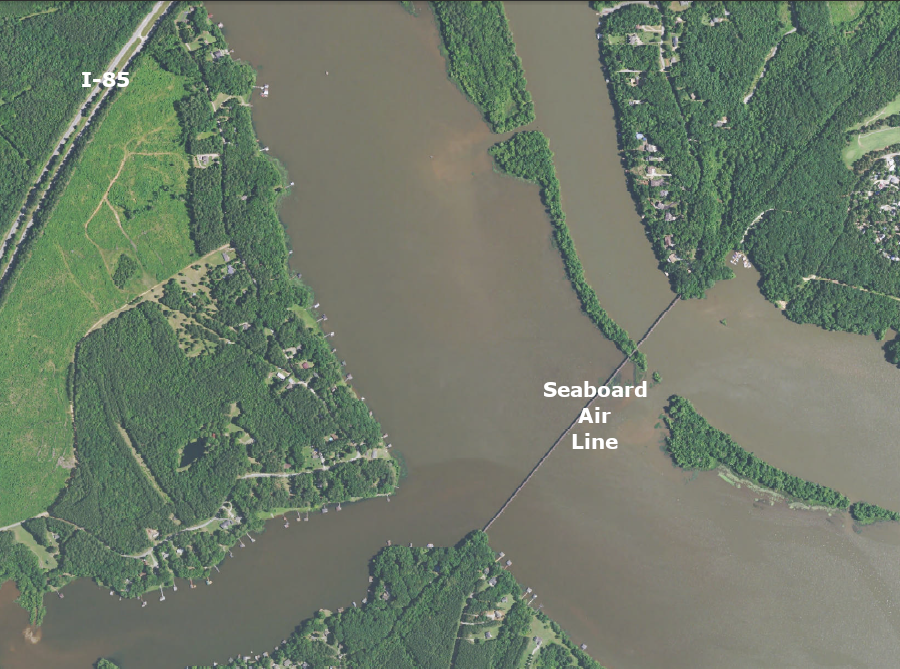

after the 1967 merger the track built by the Richmond, Petersburg & Carolina Railroad (the S Line), includng the bridge over Lake Gaston, was taken out of service
Source: ESRI, ArcGIS Online
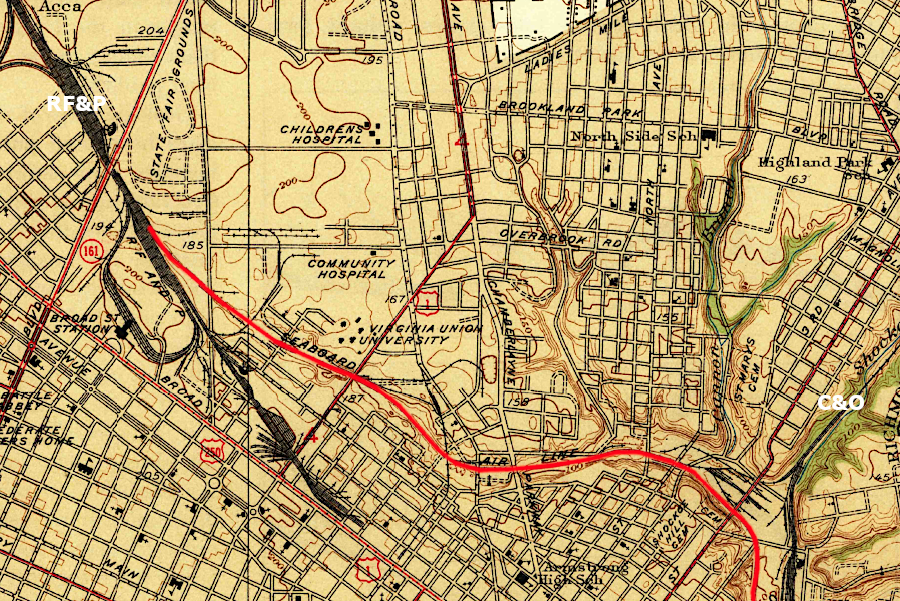
the Seaboard Air Line (red) connected with the Richmond, Fredericksburg and Potomac (RF&P) in Richmond, next to Broad Street Station
Source: US Geological Survey (USGS), Richmond, VA 1:31,680 topographic quadrangle (1939)
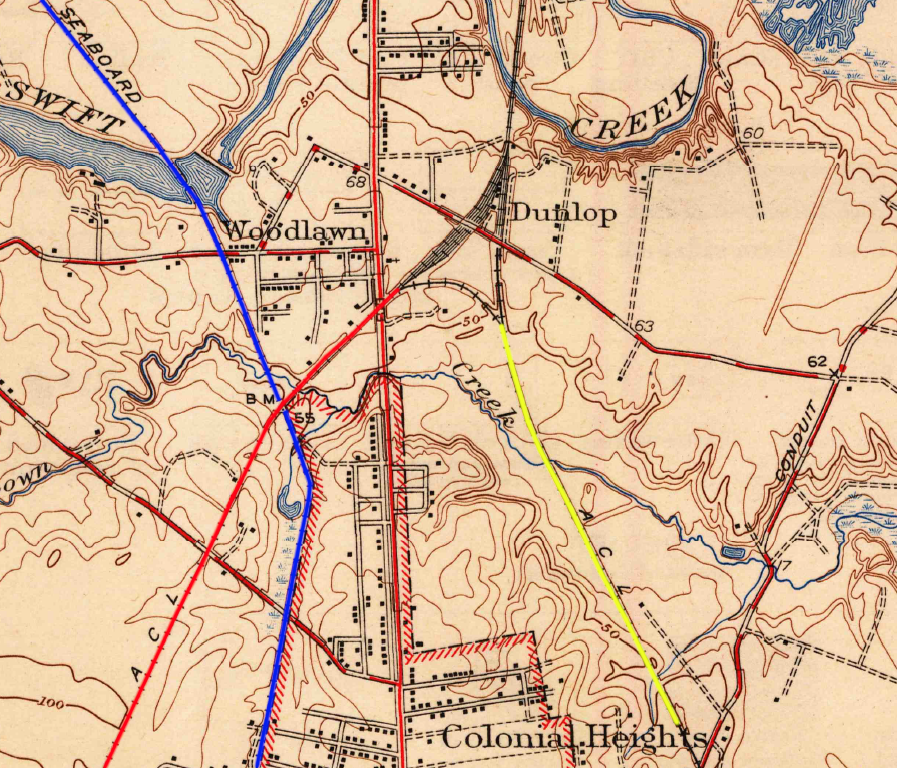
the Seaboard Air Line (blue) paralleled two segments of the Atlantic Coast Line north of Petersburg in 1944
Source: US Geological Survey (USGS), Chester, VA 1:62,500 topographic quadrangle (1944)
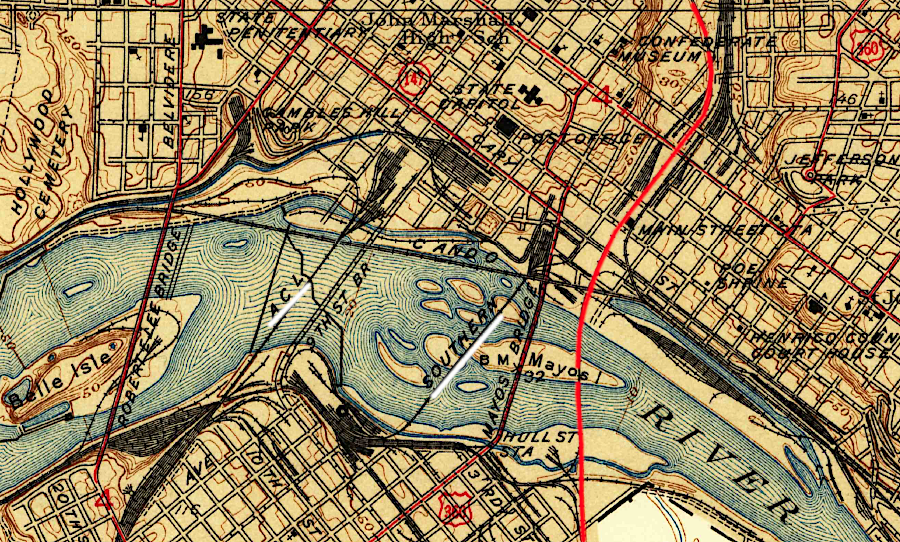
the Seaboard Air Line (red) was one of three railroads crossing the James River into downtown Richmond in 1939
Source: US Geological Survey (USGS), Richmond, VA 1:31,680 topographic quadrangle (1939)
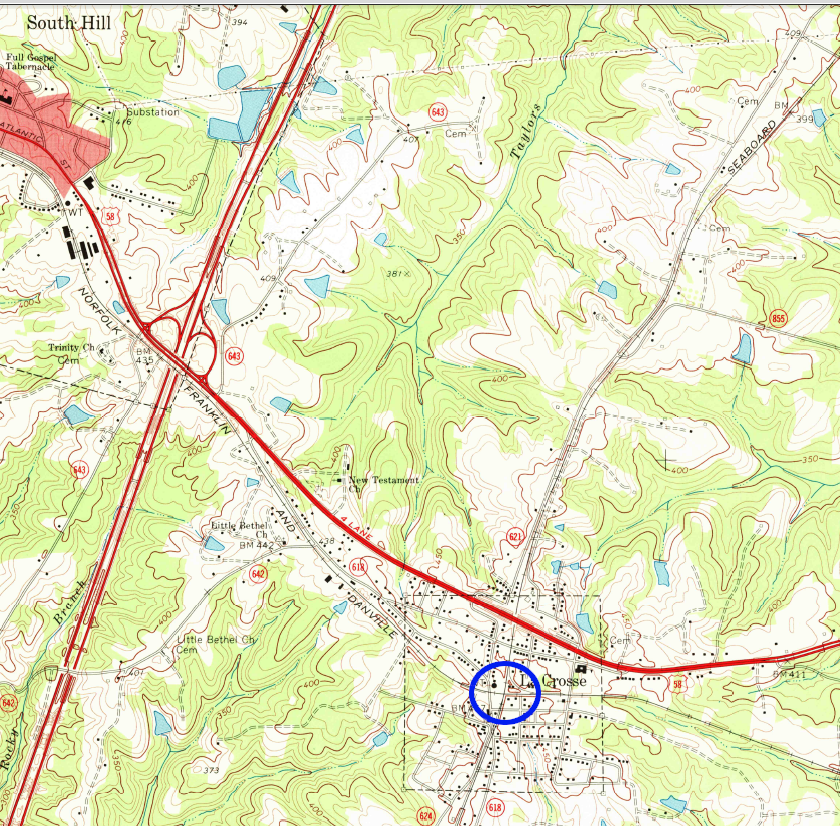
the Seaboard Air Line crossed the Atlantic and Danville/Norfolk, Franklin and Danville track at LaCrosse in 1968
Source: US Geological Survey (USGS), LaCrosse VA 1:24,000 topographic quadrangle (1968)